Impaired antiviral activity of interferon alpha against hepatitis C virus 2a in Huh-7 cells with a defective Jak-Stat pathway
- PMID: 20149251
- PMCID: PMC2831880
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-36
Impaired antiviral activity of interferon alpha against hepatitis C virus 2a in Huh-7 cells with a defective Jak-Stat pathway
Abstract
Background: The sustained virological response to interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) in individuals infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1 is only 50%, but is about 80% in patients infected with genotype 2-6 viruses. The molecular mechanisms explaining the differences in IFN-alpha responsiveness between HCV 1 and other genotypes have not been elucidated.
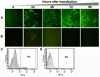
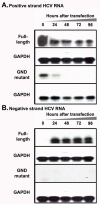
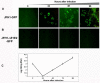
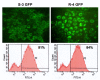
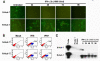
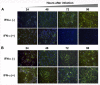
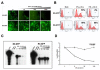
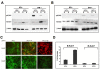
Results: Virus and host cellular factors contributing to IFN responsiveness were analyzed using a green fluorescence protein (GFP) based replication system of HCV 2a and Huh-7 cell clones that either possesses or lack a functional Jak-Stat pathway. The GFP gene was inserted into the C-terminal non-structural protein 5A of HCV 2a full-length and sub-genomic clones. Both HCV clones replicated to a high level in Huh-7 cells and could be visualized by either fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometric analysis. Huh-7 cells transfected with the GFP tagged HCV 2a genome produced infectious virus particles and the replication of fluorescence virus particles was demonstrated in naïve Huh-7.5 cells after infection. IFN-alpha effectively inhibited the replication of full-length as well as sub-genomic HCV 2a clones in Huh-7 cells with a functional Jak-Stat pathway. However, the antiviral effect of IFN-alpha against HCV 2a virus was not observed in Huh-7 cell clones with a defect in Jak-Stat signaling. HCV infection or replication did not alter IFN-alpha induced Stat phosphorylation or ISRE promoter-luciferase activity in both the sensitive and resistant Huh-7 cell clones.
Conclusions: The cellular Jak-Stat pathway is critical for a successful IFN-alpha antiviral response against HCV 2a. HCV infection or replication did not alter signaling by the Jak-Stat pathway. GFP labeled JFH1 2a replicon based stable cell lines with IFN sensitive and IFN resistant phenotypes can be used to develop new strategies to overcome IFN-resistance against hepatitis C.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Free fatty acids induce ER stress and block antiviral activity of interferon alpha against hepatitis C virus in cell culture.Virol J. 2012 Aug 3;9:143. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-143. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22863531 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ethanol on innate antiviral pathways and HCV replication in human liver cells.Virol J. 2005 Dec 2;2:89. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-89. Virol J. 2005. PMID: 16324217 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular expression of IRF9 Stat fusion protein overcomes the defective Jak-Stat signaling and inhibits HCV RNA replication.Virol J. 2010 Oct 12;7:265. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-265. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20939906 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the molecular mechanism(s) of hepatitis C virus (HCV) induced interferon resistance.Infect Genet Evol. 2013 Oct;19:113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.06.025. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Infect Genet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23831932 Review.
-
How hepatitis C virus counteracts the interferon response: the jury is still out on NS5A.Virology. 2001 May 25;284(1):1-12. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.0885. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11352662 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft supports HCV replication: a mouse model for evaluating antivirals.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jan 21;17(3):300-12. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i3.300. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21253388 Free PMC article.
-
HCV infection selectively impairs type I but not type III IFN signaling.Am J Pathol. 2014 Jan;184(1):214-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Am J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24215913 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired expression of type I and type II interferon receptors in HCV-associated chronic liver disease and liver cirrhosis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 29;9(9):e108616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108616. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25265476 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-λ Inhibits MiR-122 Transcription through a Stat3-HNF4α Inflammatory Feedback Loop in an IFN-α Resistant HCV Cell Culture System.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0141655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141655. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26657215 Free PMC article.
-
Intracytoplasmic stable expression of IgG1 antibody targeting NS3 helicase inhibits replication of highly efficient hepatitis C Virus 2a clone.Virol J. 2010 Jun 7;7:118. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-118. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20529250 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

