Vitamin D: newly discovered actions require reconsideration of physiologic requirements
- PMID: 20149679
- PMCID: PMC2880203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.01.003
Vitamin D: newly discovered actions require reconsideration of physiologic requirements
Abstract
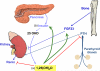
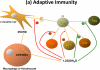
Vitamin D is not just for preventing rickets and osteomalacia. Recent findings in animal experiments, epidemiologic studies and clinical trials indicate that adequate vitamin D levels are important for cancer prevention, controlling hormone levels and regulating the immune response. Although 25 hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) levels >10 ng/ml can prevent rickets and osteomalacia, these levels are not sufficient to provide these more recently discovered clinical benefits. Rather, levels of 25OHD >30 ng/ml are generally recommended. Determining optimal levels of 25OHD and the amount of vitamin D supplementation required to achieve those levels for the numerous actions of vitamin D will only be established with additional trials. In this review, these newer applications are summarized and therapeutic considerations are provided.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Bikle D. Extra renal synthesis of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D and its Health Implications. Clin Rev in Bone and Min Metab. 2009;7:114–125.
-
- Armas LA, et al. Vitamin D2 is much less effective than vitamin D3 in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:5387–5391. - PubMed
-
- Holick MF, et al. Photosynthesis of previtamin D3 in human skin and the physiologic consequences. Science. 1980;210:203–205. - PubMed
-
- Holick MF, et al. Regulation of cutaneous previtamin D3 photosynthesis in man: skin pigment is not an essential regulator. Science. 1981;211:590–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

