Antipsychotics reverse abnormal EEG complexity in drug-naive schizophrenia: a multiscale entropy analysis
- PMID: 20149880
- PMCID: PMC2849166
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.009
Antipsychotics reverse abnormal EEG complexity in drug-naive schizophrenia: a multiscale entropy analysis
Abstract
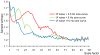
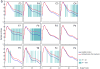
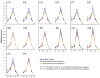
Multiscale entropy (MSE) analysis is a novel entropy-based approach for measuring dynamical complexity in physiological systems over a range of temporal scales. To evaluate this analytic approach as an aid to elucidating the pathophysiologic mechanisms in schizophrenia, we examined MSE in EEG activity in drug-naive schizophrenia subjects pre- and post-treatment with antipsychotics in comparison with traditional EEG analysis. We recorded eyes-closed resting-state EEG from frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital regions in drug-naive 22 schizophrenia and 24 age-matched healthy control subjects. Fifteen patients were re-evaluated within 2-8 weeks after the initiation of antipsychotic treatment. For each participant, MSE was calculated on one continuous 60-s epoch for each experimental session. Schizophrenia subjects showed significantly higher complexity at higher time scales (lower frequencies) than did healthy controls in fronto-centro-temporal, but not in parieto-occipital regions. Post-treatment, this higher complexity decreased to healthy control subject levels selectively in fronto-central regions, while the increased complexity in temporal sites remained higher. Comparative power analysis identified spectral slowing in frontal regions in pre-treatment schizophrenia subjects, consistent with previous findings, whereas no antipsychotic treatment effect was observed. In summary, multiscale entropy measures identified abnormal dynamical EEG signal complexity in anterior brain areas in schizophrenia that normalized selectively in fronto-central areas with antipsychotic treatment. These findings show that entropy-based analytic methods may serve as a novel approach for characterizing and understanding abnormal cortical dynamics in schizophrenia and elucidating the therapeutic mechanisms of antipsychotics.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Assessment of EEG dynamical complexity in Alzheimer's disease using multiscale entropy.Clin Neurophysiol. 2010 Sep;121(9):1438-1446. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2010.03.025. Epub 2010 Apr 18. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20400371 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of resting-state EEG-based multiscale entropy between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2024 Aug 30;134:111048. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2024.111048. Epub 2024 May 31. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38825306
-
LORETA functional imaging in antipsychotic-naive and olanzapine-, clozapine- and risperidone-treated patients with schizophrenia.Neuropsychobiology. 2008;58(1):1-10. doi: 10.1159/000154474. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Neuropsychobiology. 2008. PMID: 18781085
-
Complexity and schizophrenia.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Aug 1;45:267-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.03.015. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 22507763 Review.
-
What do ERPs and ERFs reveal about the effect of antipsychotic treatment on cognition in schizophrenia?Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(22):2573-93. doi: 10.2174/138161209788957474. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19689329 Review.
Cited by
-
Standard multiscale entropy reflects neural dynamics at mismatched temporal scales: What's signal irregularity got to do with it?PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 May 11;16(5):e1007885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007885. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32392250 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale Entropy of Electroencephalogram as a Potential Predictor for the Prognosis of Neonatal Seizures.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0144732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144732. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26658680 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted signal variability of spontaneous neural activity in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 Apr 29;12(5):3037-3049. doi: 10.1364/BOE.418921. eCollection 2021 May 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34168913 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Permutation and Multiscale Entropies for Quantification of the Brain Signal Variability in Naturalistic Scenarios.Brain Sci. 2020 Aug 6;10(8):527. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10080527. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 32781789 Free PMC article.
-
Brain connectivity studies in schizophrenia: unravelling the effects of antipsychotics.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2012 Sep;10(3):219-30. doi: 10.2174/157015912803217305. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23449679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abasolo D, Hornero R, Espino P, Poza J, Sanchez CI, de la Rosa R. Analysis of regularity in the EEG background activity of Alzheimer’s disease patients with Approximate Entropy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;116:1826–1834. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya J, Edwards J, Mamelak AN, Schuman EM. Long-range temporal correlations in the spontaneous spiking of neurons in the hippocampal-amygdala complex of humans. Neuroscience. 2005;131:547–555. - PubMed
-
- Bob P, Palus M, Susta M, Glaslova K. EEG phase synchronization in patients with paranoid schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett. 2008;447:73–77. - PubMed
-
- Breakspear M. The nonlinear theory of schizophrenia. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2006;40:20–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

