The interrelationship of dopamine D2-like receptor availability in striatal and extrastriatal brain regions in healthy humans: a principal component analysis of [18F]fallypride binding
- PMID: 20149883
- PMCID: PMC2862467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.006
The interrelationship of dopamine D2-like receptor availability in striatal and extrastriatal brain regions in healthy humans: a principal component analysis of [18F]fallypride binding
Abstract
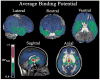
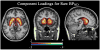
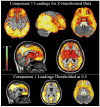
Individual differences in dopamine D2-like receptor availability arise across all brain regions expressing D2-like receptors. However, the interrelationships in receptor availability across brain regions are poorly understood. To address this issue, we examined the relationship between D2-like binding potential (BPND) across striatal and extrastriatal regions in a sample of healthy participants. PET imaging was performed with the high affinity D2/D3 ligand [18F]fallypride in 45 participants. BPND images were submitted to voxel-wise principal component analysis to determine the pattern of associations across brain regions. Individual differences in D2-like BPND were explained by three distinguishable components. A single component explained almost all of the variance within the striatum, indicating that individual differences in receptor availability vary in a homogenous manner across the caudate, putamen, and ventral striatum. Cortical BPND was only modestly related to striatal BPND and mostly loaded on a distinct component. After controlling for the general level of cortical D2-like BPND, an inverse relationship emerged between receptor availability in the striatum and the ventral temporal and ventromedial frontal cortices, suggesting possible cross-regulation of D2-like receptors in these regions. The analysis additionally revealed evidence of: (1) a distinct component involving the midbrain and limbic areas; (2) a dissociation between BPND in the medial and lateral temporal regions; and (3) a dissociation between BPND in the medial/midline and lateral thalamus. In summary, individual differences in D2-like receptor availability reflect several distinct patterns. This conclusion has significant implications for neuropsychiatric models that posit global or regionally specific relationships between dopaminergic tone and behavior.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bannon MJ, Roth RH. Pharmacology of Mesocortical Dopamine Neurons. Pharmacological Reviews. 1983;35:53–68. - PubMed
-
- Buchsbaum MS, Christian BT, Lehrer DS, Narayanan TK, Shi B, Mantil J, Kemether E, Oakes TR, Mukherjee J. D2/D3 dopamine receptor binding with [F-18]fallypride in thalamus and cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research. 2006;85:232–244. - PubMed
-
- Bull DR, Bakhtiar R, Sheehan MJ. Characterization of dopamine autoreceptors in the amygdala: a fast cyclic voltammetric study in vitro. Neuroscience Letters. 1991;134:41–44. - PubMed
-
- Clatworthy PL, Lewis SJ, Brichard L, Hong YT, Izquierdo D, Clark L, Cools R, Aigbirhio FI, Baron JC, Fryer TD, Robbins TW. Dopamine release in dissociable striatal subregions predicts the different effects of oral methylphenidate on reversal learning and spatial working memory. J Neurosci. 2009;29:4690–4696. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

