Near-isometric flattening of brain surfaces
- PMID: 20149886
- PMCID: PMC2856738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.008
Near-isometric flattening of brain surfaces
Abstract
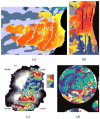
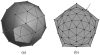
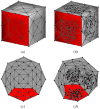
Flattened representations of brain surfaces are often used to visualize and analyze spatial patterns of structural organization and functional activity. Here, we present a set of rigorous criteria and accompanying test cases with which to evaluate flattening algorithms that attempt to preserve shortest-path distances on the original surface. We also introduce a novel flattening algorithm that is the first to satisfy all of these criteria and demonstrate its ability to produce accurate flat maps of human and macaque visual cortex. Using this algorithm, we have recently obtained results showing a remarkable, unexpected degree of consistency in the shape and topographic structure of visual cortical areas within humans and macaques, as well as between these two species.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
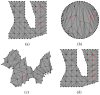


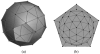

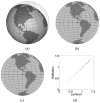


References
-
- Albright TD, Desimone R, Gross CG. Columnar organization of directionally selective cells in visual area MT of the macaque. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1984;51(1):16–31. - PubMed
-
- Angenent S, Haker S, Tannenbaum A, Kikinis R. On the Laplace-Beltrami operator and brain surface flattening. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 1999;18(8):700–711. - PubMed
-
- Annese J, Pitiot A, Dinov ID, Toga AW. A myelo-architectonic method for the structural classification of cortical areas. NeuroImage. 2004;21(1):15–26. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian M, Polimeni JR, Schwartz EL. Quasi-isometric flattening of large-scale cortical surfaces. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 2005
-
- Balasubramanian M, Polimeni JR, Schwartz EL. Quantitative evaluation and comparison of cortical flattening algorithms. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

