The efficacy of endovascular stenting in the treatment of supraclinoid internal carotid artery blister aneurysms using a stent-in-stent technique
- PMID: 20150303
- PMCID: PMC7963918
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2016
The efficacy of endovascular stenting in the treatment of supraclinoid internal carotid artery blister aneurysms using a stent-in-stent technique
Abstract
Background and purpose: Blister aneurysms of the supraclinoid ICA represent a rare but well-documented cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage. These aneurysms are difficult to detect, and their surgical treatment is challenging, with high morbidity and mortality rates. The reports currently in the literature that describe the surgical and endovascular treatment of these aneurysms offer no clear consensus on the optimal treatment. We describe a staged endovascular treatment entailing stenting using a stent-in-stent technique, as well as planned but delayed embolization as the aneurysm increases in size to allow the introduction of coils.
Materials and methods: We performed a retrospective review of all cerebral angiograms performed at our institution over an 8-month period for evaluation of subarachnoid hemorrhage, identifying 6 ICA blister aneurysms.
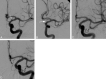
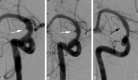
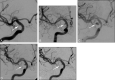
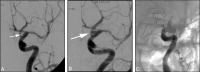
Results: All 6 blister aneurysms were located in the supraclinoid ICA. The stent-in-stent technique was used for the initial treatment of all patients. Three patients had no residual or recurrent aneurysm following initial treatment. Three patients required retreatment with coils after continued growth of the aneurysm, identified on follow-up angiography. Five patients had good recovery (average mRS score of 1), and 1 patient had poor neurologic recovery (mRS score of 3) due to a large hemorrhagic infarction.
Conclusions: Our case series suggests that staged endovascular treatment entailing the use of a stent-in-stent technique, augmented with subsequent coil embolization as necessary for progressive disease, is a viable endovascular option for treating ruptured supraclinoid blister aneurysms, allowing for parent artery preservation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utility of CT angiography in the identification and characterization of supraclinoid internal carotid artery blister aneurysms.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 Apr;31(4):640-4. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1893. Epub 2009 Nov 26. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 19942699 Free PMC article.
-
Pipeline flow diversion of ruptured blister aneurysms of the supraclinoid carotid artery using a single-device strategy.Neurosurg Focus. 2017 Jun;42(6):E11. doi: 10.3171/2017.3.FOCUS1757. Neurosurg Focus. 2017. PMID: 28565992
-
Evaluation of Enterprise Stent-Assisted Coiling and Telescoping Stent Technique as Treatment of Supraclinoid Blister Aneurysms of the Internal Carotid Artery.World Neurosurg. 2018 Feb;110:e890-e896. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.11.119. Epub 2017 Nov 28. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29191548
-
Multiple overlapping stents as monotherapy in the treatment of 'blister' pseudoaneurysms arising from the supraclinoid internal carotid artery: a single institution series and review of the literature.J Neurointerv Surg. 2014 Apr 1;6(3):184-94. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010648. Epub 2013 Mar 30. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014. PMID: 23543733 Review.
-
Current Knowledge of and Perspectives about the Pathogenesis of Blood Blister-like Aneurysms of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Review of the Literature.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Mar 3;18(9):2017-2022. doi: 10.7150/ijms.53154. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33850472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Staged treatment of a blood blister-like aneurysm with stent-assisted coiling followed by flow diverter in-stent insertion. A case report.Interv Neuroradiol. 2011 Sep;17(3):365-70. doi: 10.1177/159101991101700314. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Interv Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 22005701 Free PMC article.
-
Sole stenting with large cell stents for very small ruptured intracranial aneurysms.Interv Neuroradiol. 2014 Jan-Feb;20(1):45-53. doi: 10.15274/INR-2014-10007. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Interv Neuroradiol. 2014. PMID: 24556299 Free PMC article.
-
The management of very small/blister internal carotid artery aneurysms.Interv Neuroradiol. 2011 Dec;17(4):431-4. doi: 10.1177/159101991101700406. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Interv Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 22192546 Free PMC article.
-
Using overlapping low-profile visualized intraluminal support stent-assisted coil embolization for treating blood blister-like aneurysms of the internal carotid artery.Neurosurg Rev. 2021 Apr;44(2):1053-1060. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01284-5. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Neurosurg Rev. 2021. PMID: 32240447
-
Endovascular treatment of a ruptured blood blister-like aneurysm with a flow-diverting stent.Interv Neuroradiol. 2010 Sep;16(3):255-8. doi: 10.1177/159101991001600304. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Interv Neuroradiol. 2010. PMID: 20977856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sundt TM, Jr, Murphey F. Clip grafts for aneurysm and small vessel surgery. 3. Clinical experience in intracranial internal carotid artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg 1969;31:59–71 - PubMed
-
- Kawashima A, Okada Y, Kawamata T, et al. . Successful treatment of a blood blister-like aneurysm of the internal carotid artery by trapping with a high-flow bypass. J Clin Neurosci 2008;15:797–800 - PubMed
-
- McNeely PD, Clarke DB, Mendez I, et al. . Endovascular treatment of a “blister” aneurysm of the internal carotid artery. Can J Neurol Sci 2000;27:247–50 - PubMed
-
- Tanoue S, Kiyosue H, Matsumoto S, et al. . Ruptured “blister like” aneurysm with a pseudoaneurysm formation requiring delayed intervention with endovascular coil embolization: case report. J Neurosurg 2004;101:159–62 - PubMed
-
- Sim A, Shin Y, Cho KG, et al. . Blood blister aneurysms at nonbranching sites of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg 2006;105:400–05 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
