Bevacizumab induces regression of vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2
- PMID: 20150363
- PMCID: PMC2940556
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nop010
Bevacizumab induces regression of vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2
Abstract
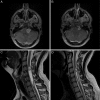
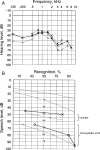
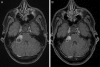
Bilateral vestibular schwannomas are the hallmark of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), and these tumors impair hearing and frequently lead to deafness. Neurosurgical intervention, the only established treatment, often damages the vestibular nerve. We report 2 cases in which treatment with bevacizumab (for 3 months in one case and 6 months in the other) induced regression of progressive vestibular schwannomas by more than 40% and substantially improved hearing in the patient treated for 6 months. Bevacizumab therapy may thus provide an effective treatment for progressive vestibular schwannomas in patients with NF2.
Figures
References
-
- Mautner VF, Lindenau M, Baser ME, et al. The neuroimaging and clinical spectrum of neurofibromatosis 2. Neurosurgery. 1996;38:880–885. - PubMed
-
- Otto SR, Brackmann DE, Hitselberger WE, Shannon RV, Kuchta J. Multi-channel auditory brain stem implant: update on performance of 61 patients. J Neurosurg. 2002;96:1063–1071. - PubMed
-
- Mathieu D, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2: an analysis of tumour control, complications, and hearing preservation rates. Neurosurgery. 2007;60:460–468. - PubMed
-
- Plotkin SR, Singh MA, O'Donnell CC, Harris GJ, McClatchey AI, Halpin C. Audiologic and radiographic response of NF2-related vestibular schwannoma to erlotinib therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008;5:487–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

