Hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance metabolic imaging: application to brain tumors
- PMID: 20150380
- PMCID: PMC2940577
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nop043
Hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance metabolic imaging: application to brain tumors
Abstract
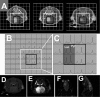
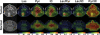
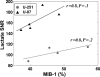
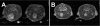
In order to compare in vivo metabolism between malignant gliomas and normal brain, (13)C magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopic imaging data were acquired from rats with human glioblastoma xenografts (U-251 MG and U-87 MG) and normal rats, following injection of hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]-pyruvate. The median signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of lactate, pyruvate, and total observed carbon-13 resonances, as well as their relative ratios, were calculated from voxels containing Gadolinium-enhanced tissue in T(1) postcontrast images for rats with tumors and from normal brain tissue for control rats. [1-(13)C]-labeled pyruvate and its metabolic product, [1-(13)C]-lactate, demonstrated significantly higher SNR in the tumor compared with normal brain tissue. Statistical tests showed significant differences in all parameters (P < .0004) between the malignant glioma tissue and normal brain. The SNR of lactate, pyruvate, and total carbon was observed to be different between the U-251 MG and U-87 MG models, which is consistent with inherent differences in the molecular characteristics of these tumors. These results suggest that hyperpolarized MR metabolic imaging may be valuable for assessing prognosis and monitoring response to therapy for patients with brain tumors.
Figures
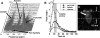

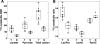


Similar articles
-
Hyperpolarized 13C MR spectroscopic imaging can be used to monitor Everolimus treatment in vivo in an orthotopic rodent model of glioblastoma.Neuroimage. 2012 Jan 2;59(1):193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.034. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 21807103 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperpolarized (13)C MR imaging detects no lactate production in mutant IDH1 gliomas: Implications for diagnosis and response monitoring.Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Jun 23;12:180-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.06.018. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2016. PMID: 27437179 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting response of rat C6 glioma tumors to radiotherapy using hyperpolarized [1- 13C]pyruvate and 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2011 Feb;65(2):557-63. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22698. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Magn Reson Med. 2011. PMID: 21264939 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor imaging using hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Magn Reson Med. 2011 Aug;66(2):505-19. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22999. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Magn Reson Med. 2011. PMID: 21661043 Review.
-
Magnetic Resonance (MR) Metabolic Imaging in Glioma.Brain Pathol. 2015 Nov;25(6):769-80. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12310. Brain Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26526945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperpolarized 13C spectroscopic imaging informs on hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and myc activity downstream of platelet-derived growth factor receptor.Cancer Res. 2010 Oct 1;70(19):7400-10. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0883. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20858719 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of therapeutic response and treatment planning for brain tumors using metabolic and physiological MRI.NMR Biomed. 2011 Jul;24(6):734-49. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1669. Epub 2011 Apr 27. NMR Biomed. 2011. PMID: 21538632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing Cerebral Metabolism with Hyperpolarized 13C Imaging after Opening the Blood-Brain Barrier with Focused Ultrasound.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Aug 4;12(15):2820-2828. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00197. Epub 2021 Jul 22. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34291630 Free PMC article.
-
MRS and MRSI guidance in molecular medicine: targeting and monitoring of choline and glucose metabolism in cancer.NMR Biomed. 2011 Jul;24(6):673-90. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1751. NMR Biomed. 2011. PMID: 21793073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A method for simultaneous echo planar imaging of hyperpolarized ¹³C pyruvate and ¹³C lactate.J Magn Reson. 2012 Apr;217:41-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.02.008. Epub 2012 Feb 24. J Magn Reson. 2012. PMID: 22405760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123(3191):309–314. - PubMed
-
- Kaibara T, Tyson RL, Sutherland GR. Human cerebral neoplasms studied using MR spectroscopy: a review. Biochem Cell Biol. 1998;76(2–3):477–486. - PubMed
-
- Herholz K, Heindel W, Luyten PR, et al. In vivo imaging of glucose consumption and lactate concentration in human gliomas. Ann Neurol. 1992;31(3):319–327. - PubMed
-
- Terpstra M, Gruetter R, High WB, et al. Lactate turnover in rat glioma measured by in vivo nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cancer Res. 1998;58(22):5083–5088. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler A, von Kienlin M, Decorps M, Remy C. High glycolytic activity in rat glioma demonstrated in vivo by correlation peak 1H magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Res. 2001;61(14):5595–5600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

