Identification of novel oxidized protein substrates and physiological partners of the mitochondrial ATP-dependent Lon-like protease Pim1
- PMID: 20150421
- PMCID: PMC2857023
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.065425
Identification of novel oxidized protein substrates and physiological partners of the mitochondrial ATP-dependent Lon-like protease Pim1
Abstract
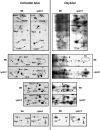
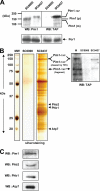
ATP-dependent proteases are currently emerging as key regulators of mitochondrial functions. Among these proteolytic systems, Pim1, a Lon-like serine protease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is involved in the control of selective protein turnover in the mitochondrial matrix. In the absence of Pim1, yeast cells have been shown to accumulate electron-dense inclusion bodies in the matrix space, to lose integrity of mitochondrial genome, and to be respiration-deficient. Because of the severity of phenotypes associated with the depletion of Pim1, this protease appears to be an essential component of the protein quality control machinery in mitochondria and to exert crucial functions during the biogenesis of this organelle. Nevertheless, its physiological substrates and partners are not fully characterized. Therefore, we used the combination of different proteomic techniques to assess the nature of oxidized protein substrates and physiological partners of Pim1 protease under non-repressing growth conditions. The results presented here supply evidence that Pim1-mediated proteolysis is required for elimination of oxidatively damaged proteins in mitochondria.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis of mitochondrial protein turnover: identification of novel substrate proteins of the matrix protease pim1.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;26(3):762-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.3.762-776.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16428434 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structure of hexameric yeast Lon protease (PIM1) highlights the importance of conserved structural elements.J Biol Chem. 2022 Mar;298(3):101694. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101694. Epub 2022 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35143841 Free PMC article.
-
Substitution of PIM1 protease in mitochondria by Escherichia coli Lon protease.J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 26;271(17):10137-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.17.10137. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8626573
-
ATP-dependent proteases controlling mitochondrial function in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Nov 30;56(9-10):825-42. doi: 10.1007/s000180050029. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 11212342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial protein homeostasis: the cooperative roles of chaperones and proteases.Res Microbiol. 2009 Nov;160(9):718-25. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.08.003. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Res Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19723579 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of Lon contributes to survival and aggressive phenotype of cancer cells through mitochondrial complex I-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Jun 20;4(6):e681. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.204. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23788038 Free PMC article.
-
Lon-dependent proteolysis in oxidative stress responses.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jul 24;207(7):e0000525. doi: 10.1128/jb.00005-25. Epub 2025 Jun 6. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40476737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of the mitochondrial Lon Protease allows adaptation to acute oxidative stress but dysregulation is associated with chronic stress, disease, and aging.Redox Biol. 2013 Feb 9;1(1):258-64. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.01.015. Redox Biol. 2013. PMID: 24024159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mitochondrial ATP-dependent Lon protease: a novel target in lymphoma death mediated by the synthetic triterpenoid CDDO and its derivatives.Blood. 2012 Apr 5;119(14):3321-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-340075. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22323447 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine desulfurase Nfs1 and Pim1 protease control levels of Isu, the Fe-S cluster biogenesis scaffold.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 26;109(26):10370-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206945109. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22689995 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

