Integrative urinary peptidomics in renal transplantation identifies biomarkers for acute rejection
- PMID: 20150539
- PMCID: PMC2844301
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009080876
Integrative urinary peptidomics in renal transplantation identifies biomarkers for acute rejection
Abstract
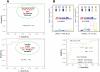
Noninvasive methods to diagnose rejection of renal allografts are unavailable. Mass spectrometry followed by multiple-reaction monitoring provides a unique approach to identify disease-specific urine peptide biomarkers. Here, we performed urine peptidomic analysis of 70 unique samples from 50 renal transplant patients and 20 controls (n = 20), identifying a specific panel of 40 peptides for acute rejection (AR). Peptide sequencing revealed suggestive mechanisms of graft injury with roles for proteolytic degradation of uromodulin (UMOD) and several collagens, including COL1A2 and COL3A1. The 40-peptide panel discriminated AR in training (n = 46) and test (n = 24) sets (area under ROC curve >0.96). Integrative analysis of transcriptional signals from paired renal transplant biopsies, matched with the urine samples, revealed coordinated transcriptional changes for the corresponding genes in addition to dysregulation of extracellular matrix proteins in AR (MMP-7, SERPING1, and TIMP1). Quantitative PCR on an independent set of 34 transplant biopsies with and without AR validated coordinated changes in expression for the corresponding genes in rejection tissue. A six-gene biomarker panel (COL1A2, COL3A1, UMOD, MMP-7, SERPING1, TIMP1) classified AR with high specificity and sensitivity (area under ROC curve = 0.98). These data suggest that changes in collagen remodeling characterize AR and that detection of the corresponding proteolytic degradation products in urine provides a noninvasive diagnostic approach.
Figures
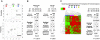


Comment in
-
Transplantation: Integrative peptidomics identifies acute renal-transplant rejection biomarkers.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010 May;6(5):249. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2010.48. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20440893 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nankivell BJ, Borrows RJ, Fung CL, O'Connell PJ, Allen RD, Chapman JR: The natural history of chronic allograft nephropathy. N Engl J Med 349: 2326– 2333, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Opelz G: Influence of treatment with cyclosporine, azathioprine and steroids on chronic allograft failure. The Collaborative Transplant Study. Kidney Int Suppl 52: S89– S92, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Marsden PA: Predicting outcomes after renal transplantation—New tools and old tools. N Engl J Med 349: 182– 184, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Li B, Hartono C, Ding R, Sharma VK, Ramaswamy R, Qian B, Serur D, Mouradian J, Schwartz JE, Suthanthiran M: Noninvasive diagnosis of renal-allograft rejection by measurement of messenger RNA for perforin and granzyme B in urine. N Engl J Med 344: 947– 954, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Sarwal M, Chua MS, Kambham N, Hsieh SC, Satterwhite T, Masek M, Salvatierra O, Jr: Molecular heterogeneity in acute renal allograft rejection identified by DNA microarray profiling. N Engl J Med 349: 125– 138, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

