Macrophage LRP-1 controls plaque cellularity by regulating efferocytosis and Akt activation
- PMID: 20150557
- PMCID: PMC2845445
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.202051
Macrophage LRP-1 controls plaque cellularity by regulating efferocytosis and Akt activation
Abstract
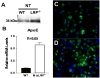
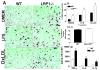
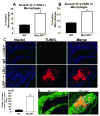
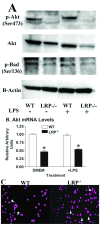
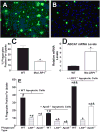
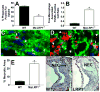
Objective: The balance between apoptosis susceptibility and efferocytosis of macrophages is central to plaque remodeling and inflammation. LRP-1 and its ligand, apolipoprotein E, have been implicated in efferocytosis and apoptosis in some cell types. We investigated the involvement of the macrophage LRP-1/apolipoprotein E axis in controlling plaque apoptosis and efferocytosis. Method and Results- LRP-1(-/-) macrophages displayed nearly 2-fold more TUNEL positivity compared to wild-type cells in the presence of DMEM alone or with either lipopolysaccharide or oxidized low-density lipoprotein. The survival kinase, phosphorylated Akt, was barely detectable in LRP-1(-/-) cells, causing decreased phosphorylated Bad and increased cleaved caspase-3. Regardless of the apoptotic stimulation and degree of cell death, LRP-1(-/-) macrophages displayed enhanced inflammation with increased IL-1 beta, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Efferocytosis of apoptotic macrophages was reduced by 60% in LRP-1(-/-) vs wild-type macrophages despite increased apolipoprotein E expression by both LRP-1(-/-) phagocytes and wild-type apoptotic cells. Compared to wild-type macrophage lesions, LRP-1(-/-) lesions had 5.7-fold more necrotic core with more dead cells not associated with macrophages.
Conclusions: Macrophage LRP-1 deficiency increases cell death and inflammation by impairing phosphorylated Akt activation and efferocytosis. Increased apolipoprotein E expression in LRP-1(-/-) macrophages suggests that the LRP-1/apolipoprotein E axis regulates the balance between apoptosis and efferocytosis, thereby preventing necrotic core formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Herz J, Clouthier DE, Hammer RE. LDL receptor-related protein internalizes and degrades uPA-PAI-1 complexes and is essential for embryo implantation. Cell. 1992;71:411–421. - PubMed
-
- Overton CD, Yancey PG, Major AS, Linton MF, Fazio S. Deletion of Macrophage LDL Receptor-Related Protein Increases Atherogenesis in the Mouse. Circ Res. 2007;100:670–677. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Gerbod-Giannone MC, Seitz H, Cui D, Thorp E, Tall AR, Matsushima GK, Tabas I. Cholesterol-induced apoptotic macrophages elicit an inflammatory response in phagocytes, which is partially attenuated by the Mer receptor. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:6707–6717. - PubMed
-
- Boullier A, Li Y, Quehenberger O, Palinski W, Tabas I, Witztum JL, Miller YI. Minimally oxidized LDL offsets the apoptotic effects of extensively oxidized LDL and free cholesterol in macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1169–1176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

