Synonymous codon usage analysis of thirty two mycobacteriophage genomes
- PMID: 20150956
- PMCID: PMC2817497
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/316936
Synonymous codon usage analysis of thirty two mycobacteriophage genomes
Abstract
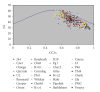
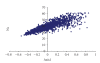
Synonymous codon usage of protein coding genes of thirty two completely sequenced mycobacteriophage genomes was studied using multivariate statistical analysis. One of the major factors influencing codon usage is identified to be compositional bias. Codons ending with either C or G are preferred in highly expressed genes among which C ending codons are highly preferred over G ending codons. A strong negative correlation between effective number of codons (Nc) and GC3s content was also observed, showing that the codon usage was effected by gene nucleotide composition. Translational selection is also identified to play a role in shaping the codon usage operative at the level of translational accuracy. High level of heterogeneity is seen among and between the genomes. Length of genes is also identified to influence the codon usage in 11 out of 32 phage genomes. Mycobacteriophage Cooper is identified to be the highly biased genome with better translation efficiency comparing well with the host specific tRNA genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Synonymous codon usage in Thermosynechococcus elongatus (cyanobacteria) identifies the factors shaping codon usage variation.Bioinformation. 2012;8(13):622-8. doi: 10.6026/97320630008622. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Bioinformation. 2012. PMID: 22829743 Free PMC article.
-
Codon Usage Optimization in the Prokaryotic Tree of Life: How Synonymous Codons Are Differentially Selected in Sequence Domains with Different Expression Levels and Degrees of Conservation.mBio. 2020 Jul 21;11(4):e00766-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00766-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32694138 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of factors shaping S. pneumoniae codon usage].Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2002;29(8):747-52. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2002. PMID: 12200868 Chinese.
-
Looking into the genome of Thermosynechococcus elongatus (thermophilic cyanobacteria) with codon selection and usage perspective.Int J Bioinform Res Appl. 2015;11(2):130-41. doi: 10.1504/IJBRA.2015.068088. Int J Bioinform Res Appl. 2015. PMID: 25786792
-
Codon usage and codon pair patterns in non-grass monocot genomes.Ann Bot. 2017 Nov 28;120(6):893-909. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcx112. Ann Bot. 2017. PMID: 29155926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cluster M mycobacteriophages Bongo, PegLeg, and Rey with unusually large repertoires of tRNA isotypes.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(5):2461-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03363-13. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24335314 Free PMC article.
-
System analysis of synonymous codon usage biases in archaeal virus genomes.J Theor Biol. 2014 Aug 21;355:128-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.03.022. Epub 2014 Mar 28. J Theor Biol. 2014. PMID: 24685889 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Genetics of Mycobacteriophages.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Mar 7;2(2):1-36. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 25328854 Free PMC article.
-
Plastome structure of 8 Calanthe s.l. species (Orchidaceae): comparative genomics, phylogenetic analysis.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Aug 3;22(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03736-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35918646 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation of codon usage pattern analysis in pancreatitis associated genes.BMC Genom Data. 2022 Nov 25;23(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12863-022-01089-z. BMC Genom Data. 2022. PMID: 36434531 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

