Regulation of chemokine production via oxidative pathway in HeLa cells
- PMID: 20150959
- PMCID: PMC2817504
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/183760
Regulation of chemokine production via oxidative pathway in HeLa cells
Abstract
Inflammation is associated with disease progression and, by largely unknown mechanisms, has been said to drive oncogenesis. At inflamed sites, neutrophils deploy a potent antimicrobial arsenal that includes proteinases, antimicrobial peptides, and ROS. Reactive oxygen species (ROSs) induce chemokines. In the present study, the concentrations of IL-8 in culture supernatants of HeLa cells treated with ROS were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. We used o-phenanthroline to deplete Fe(2+) in order to investigate the mechanisms through which ROSs induce IL-8 secretion in our system. The iron chelator o-phenanthroline effectively inhibited H(2)O(2)-induced ERK2 activation. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays showed that IL-8 protein secretion was elevated in ROS-treated HeLa cells. When Fe(2+) was removed from these cells, IL-8 secretion was inhibited. Collectively, these results indicate that Fe(2+)-mediated Erk pathway activation is an important signal transduction pathway in ROS-induced IL-8 secretion in epithelial cells.
Figures
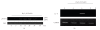


References
-
- Fialkow L, Wang Y, Downey GP. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as signaling molecules regulating neutrophil function. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2007;42(2):153–164. - PubMed
-
- Henricks PAJ, Nijkamp FP. Reactive oxygen species as mediators in asthma. Pulmonary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2001;14(6):409–421. - PubMed
-
- Dröge W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiological Reviews. 2002;82(1):47–95. - PubMed
-
- Guyton KZ, Liu Y, Gorospe M, Xu Q, Holbrook NJ. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by H2O2: role in cell survival following oxidant injury. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271(8):4138–4142. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y-M, Reed W, Wu W, Bromberg PA, Graves LM, Samet JM. Zn2+-induced IL-8 expression involves AP-1, JNK, and ERK activities in human airway epithelial cells. American Journal of Physiology. 2006;290(5):L1028–L1035. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

