Synthetic biology: tools to design, build, and optimize cellular processes
- PMID: 20150964
- PMCID: PMC2817555
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/130781
Synthetic biology: tools to design, build, and optimize cellular processes
Abstract
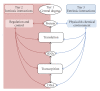
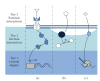
The general central dogma frames the emergent properties of life, which make biology both necessary and difficult to engineer. In a process engineering paradigm, each biological process stream and process unit is heavily influenced by regulatory interactions and interactions with the surrounding environment. Synthetic biology is developing the tools and methods that will increase control over these interactions, eventually resulting in an integrative synthetic biology that will allow ground-up cellular optimization. In this review, we attempt to contextualize the areas of synthetic biology into three tiers: (1) the process units and associated streams of the central dogma, (2) the intrinsic regulatory mechanisms, and (3) the extrinsic physical and chemical environment. Efforts at each of these three tiers attempt to control cellular systems and take advantage of emerging tools and approaches. Ultimately, it will be possible to integrate these approaches and realize the vision of integrative synthetic biology when cells are completely rewired for biotechnological goals. This review will highlight progress towards this goal as well as areas requiring further research.
Figures
References
-
- Sprinzak D, Elowitz MB. Reconstruction of genetic circuits. Nature. 2005;438(7067):443–448. - PubMed
-
- Veening J-W, Smits WK, Kuipers OP. Bistability, epigenetics, and bet-hedging in bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology. 2008;62:193–210. - PubMed
-
- Mitarai N, Sneppen K, Pedersen S. Ribosome collisions and translation efficiency: optimization by codon usage and mRNA destabilization. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2008;382(1):236–245. - PubMed
-
- Ramakrishnan V. Ribosome structure and the mechanism of translation. Cell. 2002;108(4):557–572. - PubMed
-
- Sims RJ, III, Mandal SS, Reinberg D. Recent highlights of RNA-polymerase-II-mediated transcription. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2004;16(3):263–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

