Application of the PM6 semi-empirical method to modeling proteins enhances docking accuracy of AutoDock
- PMID: 20150996
- PMCID: PMC2820493
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-2946-1-15
Application of the PM6 semi-empirical method to modeling proteins enhances docking accuracy of AutoDock
Abstract
Background: Molecular docking methods are commonly used for predicting binding modes and energies of ligands to proteins. For accurate complex geometry and binding energy estimation, an appropriate method for calculating partial charges is essential. AutoDockTools software, the interface for preparing input files for one of the most widely used docking programs AutoDock 4, utilizes the Gasteiger partial charge calculation method for both protein and ligand charge calculation. However, it has already been shown that more accurate partial charge calculation - and as a consequence, more accurate docking- can be achieved by using quantum chemical methods. For docking calculations quantum chemical partial charge calculation as a routine was only used for ligands so far. The newly developed Mozyme function of MOPAC2009 allows fast partial charge calculation of proteins by quantum mechanical semi-empirical methods. Thus, in the current study, the effect of semi-empirical quantum-mechanical partial charge calculation on docking accuracy could be investigated.
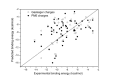
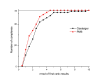
Results: The docking accuracy of AutoDock 4 using the original AutoDock scoring function was investigated on a set of 53 protein ligand complexes using Gasteiger and PM6 partial charge calculation methods. This has enabled us to compare the effect of the partial charge calculation method on docking accuracy utilizing AutoDock 4 software. Our results showed that the docking accuracy in regard to complex geometry (docking result defined as accurate when the RMSD of the first rank docking result complex is within 2 A of the experimentally determined X-ray structure) significantly increased when partial charges of the ligands and proteins were calculated with the semi-empirical PM6 method. Out of the 53 complexes analyzed in the course of our study, the geometry of 42 complexes were accurately calculated using PM6 partial charges, while the use of Gasteiger charges resulted in only 28 accurate geometries. The binding affinity estimation was not influenced by the partial charge calculation method - for more accurate binding affinity prediction development of a new scoring function for AutoDock is needed.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that the accuracy of determination of complex geometry using AutoDock 4 for docking calculation greatly increases with the use of quantum chemical partial charge calculation on both the ligands and proteins.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

