Case report: Neuropathic arthropathy of the hip as a sequela of undiagnosed tertiary syphilis
- PMID: 20151233
- PMCID: PMC2947698
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-010-1257-0
Case report: Neuropathic arthropathy of the hip as a sequela of undiagnosed tertiary syphilis
Abstract
Background: Neuropathic arthropathy is characterized by rapidly progressive bone destruction in the setting of impaired nociceptive and proprioceptive innervation to the involved joint. It is seen most commonly in the foot and ankle, secondary to peripheral neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. Other less common sites of involvement may include the knee, hip, shoulder, and spine, depending on the underlying etiology. Neuropathic arthropathy can be associated with tabes dorsalis, a unique manifestation of late, tertiary neurosyphilis that may arise in individuals with untreated syphilis many years after initial infection, and usually involves the knee, or less commonly, the hip.
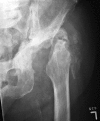
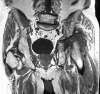
Case report: We report the case of a 73-year-old man with neuropathic arthropathy of the hip and tabes dorsalis attributable to previously undiagnosed tertiary syphilis. There was considerable delay in the diagnosis and unnecessary diagnostic testing owing to failure to consider syphilis as the cause.
Literature review: With the advent of effective antimicrobial therapy and public health campaigns, the relationship between untreated syphilis and neuropathic arthropathy has been primarily a historic point of interest. However, current epidemiologic research suggests a resurgence of syphilis in the United States, with an increased incidence of patients presenting with manifestations of tertiary syphilis from unidentified and untreated primary infections. Treatment options for neuropathic arthropathy of the hip are limited. Arthrodesis has had poor success and treatment with THA has had high complication rates.
Conclusions: Syphilis is not merely a historic cause of neuropathic arthropathy. Neurosyphilis and tabes dorsalis should be considered in the differential diagnosis for patients presenting with rapid joint destruction consistent with Charcot arthropathy and no other apparent cause.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tabetic arthropathy revealing neurosyphilis: a new observation.Pan Afr Med J. 2014 Jul 5;18:198. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2014.18.198.4893. eCollection 2014. Pan Afr Med J. 2014. PMID: 25419325 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multifocal neuropathic arthropathy in patient with undiagnosed neurosyphilis: A case report.Int J STD AIDS. 2017 Jun;28(7):729-731. doi: 10.1177/0956462416679068. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Int J STD AIDS. 2017. PMID: 27810982
-
A patient with multifocal tabetic arthropathy: a case report and review of literature.Sex Transm Dis. 2013 Mar;40(3):251-7. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31827df2c6. Sex Transm Dis. 2013. PMID: 23403606 Review.
-
Multiple neuropathic arthropathy in a patient with syphilis.Clin Rheumatol. 1985 Sep;4(3):348-52. doi: 10.1007/BF02031621. Clin Rheumatol. 1985. PMID: 4064592
-
Neuropathic arthropathy: a forgotten diagnosis? Two recent cases involving the hip.Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1999 May;66(5):284-7. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1999. PMID: 10380262 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosing Tabes Dorsalis in HIV-Negative Patients: Clinical Features, Neuroimaging, and Laboratory Insights in the Modern Antibiotic Era.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jun 21;17:2567-2577. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S464581. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38919834 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, progressive neuropathic arthropathy of the hip in a patient co-infected with human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis C virus and tertiary syphilis: case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 6;11:159. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-11-159. BMC Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21645338 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Total Knee Arthroplasty and Ankle Arthrodesis for Charcot Neuroarthropathy.Case Rep Orthop. 2019 Dec 7;2019:6136409. doi: 10.1155/2019/6136409. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Orthop. 2019. PMID: 31885983 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty for Charcot Arthropathy After Cauda Equine Syndrome: A Case Report.J Med Cases. 2020 Feb;11(2):49-53. doi: 10.14740/jmc3412. Epub 2020 Feb 28. J Med Cases. 2020. PMID: 34434361 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-CT evaluation of historical human skulls presenting signs of syphilitic infection.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021 Jun;133(11-12):602-609. doi: 10.1007/s00508-021-01832-z. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 33791870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allali F, Rahmouni R, Hajjaj-Hassouni N. Tabetic arthropathy: a report of 43 cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25:858–860. - PubMed
-
- Alpert SW, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. Neuropathic arthropathy: review of current knowledge. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996;4:100–108. - PubMed
-
- Avimadje AM, Pellieux S, Goupille P, Zerkak D, Valat JP, Fouquet B. Destructive hip disease complicating traumatic paraplegia. Joint Bone Spine. 2000;67:334–336. - PubMed
-
- Bruckner FE, Howell A. Neuropathic joints. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1972;2:47–69. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases surveillance, 2007: syphilis. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/std/stats07/syphilis.htm. Accessed May 14, 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

