Expression of cell cycle proteins in male breast carcinoma
- PMID: 20152033
- PMCID: PMC2829567
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-8-10
Expression of cell cycle proteins in male breast carcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Male breast cancer (MBC) is a rare, yet potentially aggressive disease. Although literature regarding female breast cancer (FBC) is extensive, little is known about the etiopathogenesis of male breast cancer. Studies from our laboratory show that MBCs have a distinct immunophenotypic profile, suggesting that the etiopathogenesis of MBC is different from FBCs. The aim of this study was to evaluate and correlate the immunohistochemical expression of cell cycle proteins in male breast carcinoma to significant clinico-biological endpoints.
Methods: 75 cases of MBC were identified using the records of the Saskatchewan Cancer Agency over 26 years (1970-1996). Cases were reviewed and analyzed for the immunohistochemical expression of PCNA, Ki67, p27, p16, p57, p21, cyclin-D1 and c-myc and correlated to clinico-biological endpoints of tumor size, node status, stage of the disease, and disease free survival (DFS).
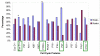
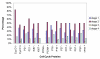
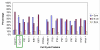
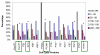
Results: Decreased DFS was observed in the majority of tumors that overexpressed PCNA (98%, p = 0.004). The overexpression of PCNA was inversely correlated to the expression of Ki67 which was predominantly negative (78.3%). Cyclin D1 was overexpressed in 83.7% of cases. Cyclin D1 positive tumors were smaller than 2 cm (55.6%, p = 0.005), had a low incidence of lymph node metastasis (38.2%, p = 0.04) and were associated with increased DFS of >150 months (p = 0.04). Overexpression of c-myc (90%) was linked with a higher incidence of node negativity (58.3%, p = 0.006) and increased DFS (p = 0.04). p27 over expression was associated with decreased lymph node metastasis (p = 0.04). P21 and p57 positive tumors were related to decreased DFS (p = 0.04). Though p16 was overexpressed in 76.6%, this did not reach statistical significance with DFS (p = 0.06) or nodal status (p = 0.07).
Conclusion: Aberrant cell cycle protein expression supports our view that these are important pathways involved in the etiopathogenesis of MBC. Tumors with overexpression of Cyclin D1 and c-myc had better outcomes, in contrast to tumors with overexpression of p21, p57, and PCNA with significantly worse outcomes. P27 appears to be a predictive marker for lymph nodal status. Such observation strongly suggests that dysregulation of cell cycle proteins may play a unique role in the initiation and progression of disease in male breast cancer. Such findings open up new avenues for the treatment of MBC as a suitable candidate for novel CDK-based anticancer therapies in the future.
Figures
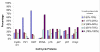
References
-
- Muir D, Kanthan R, Kanthan SC. Male Versus Female Breast Cancers. A Population-Based Comparative Immunohistochemical Analysis. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine. 2003;127(1):36–41. - PubMed
-
- Weiss JR, Moysich KB, Swede H. Epidemiology of Male Breast Cancer. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 2005;14(1):20–26. - PubMed
-
- Giordano SH, Buzdar AU, Hortobagyi GN. Breast Cancer in Men. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2002;137(8):678–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

