Preparing for the first breath: genetic and cellular mechanisms in lung development
- PMID: 20152174
- PMCID: PMC3736813
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.12.010
Preparing for the first breath: genetic and cellular mechanisms in lung development
Abstract
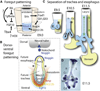
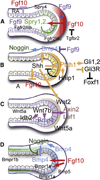
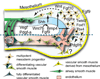
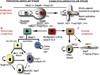
The mammalian respiratory system--the trachea and the lungs--arises from the anterior foregut through a sequence of morphogenetic events involving reciprocal endodermal-mesodermal interactions. The lung itself consists of two highly branched, tree-like systems--the airways and the vasculature--that develop in a coordinated way from the primary bud stage to the generation of millions of alveolar gas exchange units. We are beginning to understand some of the molecular and cellular mechanisms that underlie critical processes such as branching morphogenesis, vascular development, and the differentiation of multipotent progenitor populations. Nevertheless, many gaps remain in our knowledge, the filling of which is essential for understanding respiratory disorders, congenital defects in human neonates, and how the disruption of morphogenetic programs early in lung development can lead to deficiencies that persist throughout life.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Affolter M, Basler K. The Decapentaplegic morphogen gradient: from pattern formation to growth regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:663–674. - PubMed
-
- Affolter M, Caussinus E. Tracheal branching morphogenesis in Drosophila: new insights into cell behaviour and organ architecture. Development. 2008;135:2055–2064. - PubMed
-
- Alejandre-Alcázar MA, Shalamanov PD, Amarie OV, Sevilla-Pérez J, Seeger W, Eickelberg O, Morty RE. Temporal and spatial regulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in late lung development. Dev. Dyn. 2007;236:2825–2835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

