Effect of gastric bypass surgery on the incretins
- PMID: 20152736
- PMCID: PMC2842993
- DOI: 10.1016/S1262-3636(09)73458-5
Effect of gastric bypass surgery on the incretins
Abstract
Aims: Our studies were designed to understand the role of the gut hormones incretins GLP-1 and GIP on diabetes remission after gastric bypass surgery (GBP).
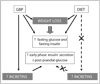
Methods: Morbidly obese patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) were studied before and 1, 6, 12, 24 and 36 months after GBP. A matched group of patients were studied before and after a diet-induced 10 kg weight loss, equivalent to the weight loss 1 month after GBP. All patients underwent an oral glucose tolerance test and an isoglycaemic glucose intravenous challenge to measure the incretin effect.
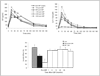
Results: Post-prandial GLP-1 and GIP levels increase after GBP and the incretin effect on insulin secretion normalizes to the level of non diabetic controls. In addition, the pattern of insulin secretion in response to oral glucose changes after GBP, with recovery of the early phase, and post-prandial glucose levels decrease significantly. These changes were not seen after an equivalent weight loss by diet. The changes in incretin levels and effect observed at 1 month are long lasting and persist up to 3 years after the surgery. The improved insulin release and glucose tolerance after GBP were shown by others to be blocked by the administration of a GLP-1 antagonist in rodents, demonstrating that these metabolic changes are, in part, GLP-1 dependent.
Conclusion: Although sustained and significant weight loss is likely to be the key mediator of diabetes remission after GBP, the changes of incretins improve the early phase of insulin secretion and post-prandial glucose levels, and contribute to the better glucose tolerance.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported no conèict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K, et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724–1737. - PubMed
-
- Dixon JB, O'Brien PE, Playfair J, Chapman L, Schachter LM, Skinner S, et al. Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2008;299:316–323. - PubMed
-
- Rossetti L, Giaccari A, DeFronzo RA. Glucose toxicity. Diabetes Care. 1990;13:610–630. - PubMed
-
- Leahy JL, Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC. Beta-cell dysfunction induced by chronic hyperglycemia. Current ideas on mechanism of impaired glucose-induced insulin secretion. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:442–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

