Bazooka regulates microtubule organization and spatial restriction of germ plasm assembly in the Drosophila oocyte
- PMID: 20152826
- PMCID: PMC2854266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.02.006
Bazooka regulates microtubule organization and spatial restriction of germ plasm assembly in the Drosophila oocyte
Abstract
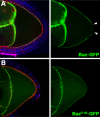
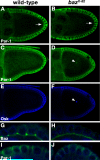
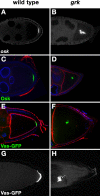
Localization of the germ plasm to the posterior of the Drosophila oocyte is required for anteroposterior patterning and germ cell development during embryogenesis. While mechanisms governing the localization of individual germ plasm components have been elucidated, the process by which germ plasm assembly is restricted to the posterior pole is poorly understood. In this study, we identify a novel allele of bazooka (baz), the Drosophila homolog of Par-3, which has allowed the analysis of baz function throughout oogenesis. We demonstrate that baz is required for spatial restriction of the germ plasm and axis patterning, and we uncover multiple requirements for baz in regulating the organization of the oocyte microtubule cytoskeleton. Our results suggest that distinct cortical domains established by Par proteins polarize the oocyte through differential effects on microtubule organization. We further show that microtubule plus-end enrichment is sufficient to drive germ plasm assembly even at a distance from the oocyte cortex, suggesting that control of microtubule organization is critical not only for the localization of germ plasm components to the posterior of the oocyte but also for the restriction of germ plasm assembly to the posterior pole.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Benton R, Palacios IM, St Johnston D. Drosophila 14-3-3/PAR-5 is an essential mediator of PAR-1 function in axis formation. Dev. Cell. 2002;3:659–671. - PubMed
-
- Benton R, St Johnston D. A conserved oligomerization domain in Drosophila Bazooka/PAR-3 is important for apical localization and epithelial polarity. Curr. Biol. 2003a;13:1330–1334. - PubMed
-
- Benton R, St Johnston D. Drosophila PAR-1 and 14-3-3 inhibit Bazooka/PAR-3 to establish complementary cortical domains in polarized cells. Cell. 2003b;115:691–704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

