Emx2 and early hair cell development in the mouse inner ear
- PMID: 20152827
- PMCID: PMC2877772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.02.004
Emx2 and early hair cell development in the mouse inner ear
Abstract
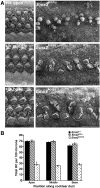
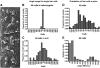
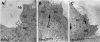
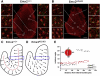
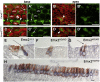
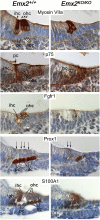
Emx2 is a homeodomain protein that plays a critical role in inner ear development. Homozygous null mice die at birth with a range of defects in the CNS, renal system and skeleton. The cochlea is shorter than normal with about 60% fewer auditory hair cells. It appears to lack outer hair cells and some supporting cells are either absent or fail to differentiate. Many of the hair cells differentiate in pairs and although their hair bundles develop normally their planar cell polarity is compromised. Measurements of cell polarity suggest that classic planar cell polarity molecules are not directly influenced by Emx2 and that polarity is compromised by developmental defects in the sensory precursor population or by defects in epithelial cues for cell alignment. Planar cell polarity is normal in the vestibular epithelia although polarity reversal across the striola is absent in both the utricular and saccular maculae. In contrast, cochlear hair cell polarity is disorganized. The expression domain for Bmp4 is expanded and Fgfr1 and Prox1 are expressed in fewer cells in the cochlear sensory epithelium of Emx2 null mice. We conclude that Emx2 regulates early developmental events that balance cell proliferation and differentiation in the sensory precursor population.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Emx2 lineage tracing reveals antecedent patterns of planar polarity in the mouse inner ear.Development. 2024 May 15;151(10):dev202425. doi: 10.1242/dev.202425. Epub 2024 May 16. Development. 2024. PMID: 38682291 Free PMC article.
-
Prox1 interacts with Atoh1 and Gfi1, and regulates cellular differentiation in the inner ear sensory epithelia.Dev Biol. 2008 Oct 1;322(1):33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.07.004. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18652815
-
Hes1 and Hes5 activities are required for the normal development of the hair cells in the mammalian inner ear.J Neurosci. 2001 Jul 1;21(13):4712-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-13-04712.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11425898 Free PMC article.
-
A balance of form and function: planar polarity and development of the vestibular maculae.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 May;24(5):490-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23507521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atoh1 and other related key regulators in the development of auditory sensory epithelium in the mammalian inner ear: function and interplay.Dev Biol. 2019 Feb 15;446(2):133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.12.025. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30605626 Review.
Cited by
-
LIN28B/let-7 control the ability of neonatal murine auditory supporting cells to generate hair cells through mTOR signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):22225-22236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000417117. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32826333 Free PMC article.
-
Fgf8 genetic labeling reveals the early specification of vestibular hair cell type in mouse utricle.Development. 2020 Nov 19;147(22):dev192849. doi: 10.1242/dev.192849. Development. 2020. PMID: 33046506 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Selective Scans Detect Genes Associated With Important Phenotypic Traits in Sheep (Ovis aries).Front Genet. 2021 Nov 18;12:738879. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.738879. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34868210 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into regulation and function of planar polarity in the inner ear.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Sep 14;709:134373. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134373. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31295539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genetics of hair cell development and regeneration.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2013 Jul 8;36:361-81. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062012-170309. Epub 2013 May 29. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23724999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boncinelli E. Homeobox genes and disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1997;7:331–337. - PubMed
-
- Brown S.D., Hardisty-Hughes R.E., Mburu P. Quiet as a mouse: dissecting the molecular and genetic basis of hearing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008;9:277–290. - PubMed
-
- Cecchi C. Emx2: a gene responsible for cortical development, regionalization and area specification. Gene. 2002;291:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Cecchi C., Boncinelli E. Emx homeogenes and mouse brain development. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:347–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

