A higher-order complex containing AF4 and ENL family proteins with P-TEFb facilitates oncogenic and physiologic MLL-dependent transcription
- PMID: 20153263
- PMCID: PMC2824033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.040
A higher-order complex containing AF4 and ENL family proteins with P-TEFb facilitates oncogenic and physiologic MLL-dependent transcription
Abstract
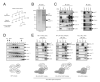
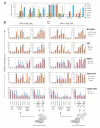
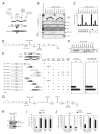
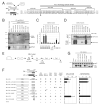
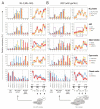
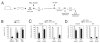
AF4 and ENL family proteins are frequently fused with MLL, and they comprise a higher order complex (designated AEP) containing the P-TEFb transcription elongation factor. Here, we show that AEP is normally recruited to MLL-target chromatin to facilitate transcription. In contrast, MLL oncoproteins fused with AEP components constitutively form MLL/AEP hybrid complexes to cause sustained target gene expression, which leads to transformation of hematopoietic progenitors. Furthermore, MLL-AF6, an MLL fusion with a cytoplasmic protein, does not form such hybrid complexes, but nevertheless constitutively recruits AEP to target chromatin via unknown alternative mechanisms. Thus, AEP recruitment is an integral part of both physiological and pathological MLL-dependent transcriptional pathways. Bypass of its normal recruitment mechanisms is the strategy most frequently used by MLL oncoproteins.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bitoun E, Oliver PL, Davies KE. The mixed-lineage leukemia fusion partner AF4 stimulates RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation and mediates coordinated chromatin remodeling. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:92–106. - PubMed
-
- Cheung N, Chan LC, Thompson A, Cleary ML, So CW. Protein arginine-methyltransferase-dependent oncogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:1208–1215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

