Size-dependent neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid oligomers
- PMID: 20153288
- PMCID: PMC2853175
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.02.001
Size-dependent neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid oligomers
Abstract
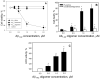
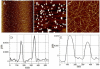
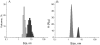
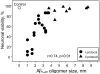
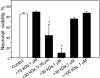
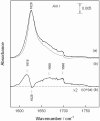
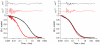
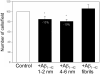
The link between the size of soluble amyloid beta (Abeta) oligomers and their toxicity to rat cerebellar granule cells (CGC) was investigated. Variation in conditions during in vitro oligomerization of Abeta(1-42) resulted in peptide assemblies with different particle size as measured by atomic force microscopy and confirmed by dynamic light scattering and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Small oligomers of Abeta(1-42) with a mean particle z-height of 1-2 nm exhibited propensity to bind to phospholipid vesicles and they were the most toxic species that induced rapid neuronal necrosis at submicromolar concentrations whereas the bigger aggregates (z-height above 4-5 nm) did not bind vesicles and did not cause detectable neuronal death. A similar neurotoxic pattern was also observed in primary cultures of cortex neurons whereas Abeta(1-42) oligomers, monomers and fibrils were non-toxic to glial cells in CGC cultures or macrophage J774 cells. However, both oligomeric forms of Abeta(1-42) induced reduction of neuronal cell densities in the CGC cultures.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Chen YR, Glabe CG. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006;281:24414–24422. - PubMed
-
- McLean CA, Cherny RA, Fraser FW, Fuller SJ, Smith MJ, Beyreuther K, Bush AI, Masters CL. Annals of Neurology. 1999;46:860–866. - PubMed
-
- Cleary JP. Nat.Neurosci. 2005;8:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Lesne S, Koh MT, Kotilinek L, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Yang A, Gallagher M, Ashe KH. Nature. 2006;440:352–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

