Targeting anoikis resistance in prostate cancer metastasis
- PMID: 20153362
- PMCID: PMC2988681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2010.02.001
Targeting anoikis resistance in prostate cancer metastasis
Abstract
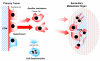
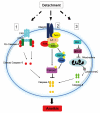
Anoikis is a mode of apoptotic cell death, consequential to insufficient cell-matrix interactions and a critical player in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. The events involved in tumor cell progression toward metastasis potential are mediated by integrins, which upon engagement with components of the extracellular matrix (ECM), reorganize to form adhesion complexes. Targeting apoptotic players is of immense therapeutic significance since resistance to apoptosis is not only critical in conferring therapeutic failure to standard treatment strategies, but anoikis (apoptosis upon loss of anchorage and detachment from ECM) also plays an important role in angiogenesis and metastasis. The ability to survive in the absence of adhesion to the ECM, enables tumor cells to disseminate from the primary tumor site, invade a distant site and establish a metastatic lesion. Tumor cells can escape from detachment-induced apoptosis by controlling anoikis pathways, including the extrinsic death receptor pathway and the ECM-integrin mediated cell survival pathway. Considering the functional promiscuity of individual signaling effectors, it is critical to dissect the molecular networks mechanistically driving tumor cells to evade anoikis and embark on a metastatic spread. Resistance to die via anoikis dictates tumor cell survival and provides a molecular basis for therapeutic targeting of metastatic prostate cancer. Further dissection of critical anoikis signaling events will enable the therapeutic optimization of anoikis targeting to impair prostate cancer metastasis prior to its initiation. This review will discuss the molecular understanding of anoikis regulation in the tumor microenvironment and the in vivo pharmacological implementation of a novel class of antitumor-drugs to optimize apoptotic-based therapeutic targeting, bypassing anoikis-resistance to impair prostate cancer progression to metastasis. Potential combination strategies targeting tumor vascularity (via anoikis) and impairing tumor initiation (via "classic" apoptosis), provide strong therapeutic promise for metastatic prostate cancer by preventing the onset of metastasis.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Amantana A, London CA, Iversen PL, Devi GR. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibition induces apoptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity in human prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004;3:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Attwell S, Roskelley C, Dedhar S. The integrin-linked kinase (ILK) suppresses anoikis. Oncogene. 2000;19:3811–3815. - PubMed
-
- Barrallo-Gimeno A, Nieto MA. The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development. 2005;132:3151–361. - PubMed
-
- Biswas SC, Greene LA. Nerve growth factor (NGF) down-regulates the Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) domain-only protein Bim and suppresses its proapoptotic activity by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:49511–49516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

