Effects of tempol and redox-cycling nitroxides in models of oxidative stress
- PMID: 20153367
- PMCID: PMC2854323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.01.003
Effects of tempol and redox-cycling nitroxides in models of oxidative stress
Abstract
Tempol is a redox-cycling nitroxide that promotes the metabolism of many reactive oxygen species (ROS) and improves nitric oxide bioavailability. It has been studied extensively in animal models of oxidative stress. Tempol has been shown to preserve mitochondria against oxidative damage and improve tissue oxygenation. Tempol improved insulin responsiveness in models of diabetes mellitus and improved the dyslipidemia, reduced the weight gain and prevented diastolic dysfunction and heart failure in fat-fed models of the metabolic syndrome. Tempol protected many organs, including the heart and brain, from ischemia/reperfusion damage. Tempol prevented podocyte damage, glomerulosclerosis, proteinuria and progressive loss of renal function in models of salt and mineralocorticosteroid excess. It reduced brain or spinal cord damage after ischemia or trauma and exerted a spinal analgesic action. Tempol improved survival in several models of shock. It protected normal cells from radiation while maintaining radiation sensitivity of tumor cells. Its paradoxical pro-oxidant action in tumor cells accounted for a reduction in spontaneous tumor formation. Tempol was effective in some models of neurodegeneration. Thus, tempol has been effective in preventing several of the adverse consequences of oxidative stress and inflammation that underlie radiation damage and many of the diseases associated with aging. Indeed, tempol given from birth prolonged the life span of normal mice. However, presently tempol has been used only in human subjects as a topical agent to prevent radiation-induced alopecia.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
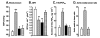
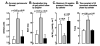
References
-
- Adeagbo AS, Joshua IG, Falkner C, Matheson PJ. Tempol, an antioxidant, restores endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated vasodilation during hypertension. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;481:91–100. - PubMed
-
- Adler A, Messina E, Sherman B, Wang Z, Huang H, Linke A, et al. NAD(P)H oxidase-generated superoxide anion accounts for reduced control of myocardial O2 consumption by NO in old Fischer 344 rats. Am J Physiol. 2003;285:H1015–1022. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama N, Umeda IO, Sogo S, Nishigori H, Tsujimoto M, Natori S. 5-S-GAD, a novel radical scavenging compound, prevents lens opacity development. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;46:511–519. - PubMed
-
- Alpert E, Altman H, Totary H, Gruzman A, Barnea D, Barash V, et al. 4-Hydroxy tempol-induced impairment of mitochondrial function and augmentation of glucose transport in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;67:1985–1995. - PubMed
-
- Ando K, Fujita T. Metabolic syndrome and oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;47:213–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

