Altered lipid A structures and polymyxin hypersensitivity of Rhizobium etli mutants lacking the LpxE and LpxF phosphatases
- PMID: 20153447
- PMCID: PMC2839054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.02.001
Altered lipid A structures and polymyxin hypersensitivity of Rhizobium etli mutants lacking the LpxE and LpxF phosphatases
Abstract
The lipid A of Rhizobium etli, a nitrogen-fixing plant endosymbiont, displays significant structural differences when compared to that of Escherichia coli. An especially striking feature of R. etli lipid A is that it lacks both the 1- and 4'-phosphate groups. The 4'-phosphate moiety of the distal glucosamine unit is replaced with a galacturonic acid residue. The dephosphorylated proximal unit is present as a mixture of the glucosamine hemiacetal and an oxidized 2-aminogluconate derivative. Distinct lipid A phosphatases directed to the 1 or the 4'-positions have been identified previously in extracts of R. etli and Rhizobium leguminosarum. The corresponding structural genes, lpxE and lpxF, respectively, have also been identified. Here, we describe the isolation and characterization of R. etli deletion mutants in each of these phosphatase genes and the construction of a double phosphatase mutant. Mass spectrometry confirmed that the mutant strains completely lacked the wild-type lipid A species and accumulated the expected phosphate-containing derivatives. Moreover, radiochemical analysis revealed that phosphatase activity was absent in membranes prepared from the mutants. Our results indicate that LpxE and LpxF are solely responsible for selectively dephosphorylating the lipid A molecules of R. etli. All the mutant strains showed an increased sensitivity to polymyxin relative to the wild-type. However, despite the presence of altered lipid A species containing one or both phosphate groups, all the phosphatase mutants formed nitrogen-fixing nodules on Phaseolus vulgaris. Therefore, the dephosphorylation of lipid A molecules in R. etli is not required for nodulation but may instead play a role in protecting the bacteria from cationic antimicrobial peptides or other immune responses of plants.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

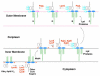


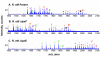
 = + 28 28)
= + 28 28)  = +14 α = (−86 and + 28) ¢ = −14 π = (−86 and + 14) ∂ = (−86 and + 14 and + 28) λ = (−86 and −14).
= +14 α = (−86 and + 28) ¢ = −14 π = (−86 and + 14) ∂ = (−86 and + 14 and + 28) λ = (−86 and −14).
 = + 28 28)
= + 28 28)  = +14 β = (+28 and +14) ¢ = −14 π = (−86 and + 14) α = (−86 and + 28) ∂ = (−86 and + 14 and + 28) λ = (−86 and −14).
= +14 β = (+28 and +14) ¢ = −14 π = (−86 and + 14) α = (−86 and + 28) ∂ = (−86 and + 14 and + 28) λ = (−86 and −14).

References
-
- Russell JA. Management of sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;355:1699–1713. - PubMed
-
- Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H, Lee JO. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 2009;458:1191–1195. - PubMed
-
- Rietschel ET, Kirikae T, Schade FU, Mamat U, Schmidt G, Loppnow H, Ulmer AJ, Zähringer U, Seydel U, Di Padova F, Schreier M, Brade H. Bacterial endotoxin: molecular relationships of structure to activity and function. FASEB Journal. 1994;8:217–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

