Evidence for a role of immunoproteasomes in regulating cardiac muscle mass in diabetic mice
- PMID: 20153750
- PMCID: PMC2883685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.02.007
Evidence for a role of immunoproteasomes in regulating cardiac muscle mass in diabetic mice
Abstract
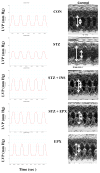
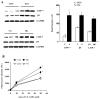
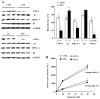
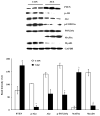
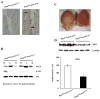
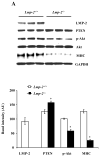
The ubiquitin-proteasome system plays an important role in regulating muscle mass. Inducible immunoproteasome subunits LMP-2 and LMP-7 are constitutively expressed in the heart; however, their regulation and functions are poorly understood. We here investigated the hypothesis that immunoproteasomes regulate cardiac muscle mass in diabetic mice. Type 1 diabetes was induced in wildtype mice by streptozotocin. After hyperglycemia developed, insulin and the proteasome inhibitor epoxomicin were used to treat diabetic mice for 6weeks. Isolated mouse hearts were perfused with control or high glucose solution. Catalytic proteasome beta-subunits and proteolytic activities were analyzed in the heart by immunoblotting and fluorogenic peptide degradation assays, respectively. Insulin and epoxomicin blocked loss of heart weight and improved cardiac function in diabetic mice. LMP-7 and its corresponding chymotryptic-like proteasome activity were increased in diabetic hearts and high glucose-treated hearts. Myosin heavy chain protein was decreased in diabetic hearts, which was largely reversed by epoxomicin. High glucose decreased LMP-2 protein levels in perfused hearts. In diabetic hearts, LMP-2 expression was downregulated whereas expression of the phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) and the muscle atrophy F-box were upregulated. Moreover, mice with muscle-specific knockout of PTEN gene demonstrated increased cardiac muscle mass, while mice with LMP-2 deficiency demonstrated PTEN accumulation, muscle mass loss, and contractile impairment in the heart. Therefore, we concluded that high glucose regulates immunoproteasome subunits and modifies proteasome activities in the heart, and that dysregulated immunoproteasome subunits may mediate loss of cardiac muscle mass in experimental diabetic mice.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
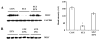

Comment in
-
Non-antigen processing immunoproteasomes in diabetic hearts?J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jul;49(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.03.024. Epub 2010 Apr 9. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20382154 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Ischemic preconditioning-induced cardioprotection is lost in mice with immunoproteasome subunit low molecular mass polypeptide-2 deficiency.FASEB J. 2008 Dec;22(12):4248-57. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-105940. Epub 2008 Aug 26. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18728217 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac muscle protein catabolism in diabetes mellitus: activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by insulin deficiency.Endocrinology. 2008 Nov;149(11):5384-90. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0132. Epub 2008 Jul 24. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18653708 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway in heart vs skeletal muscle: effects of acute diabetes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Oct 5;276(3):1255-60. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3609. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 11027619
-
Hyperglycemia impairs proteasome function by methylglyoxal.Diabetes. 2010 Mar;59(3):670-8. doi: 10.2337/db08-1565. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20009088 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac proteasome functional insufficiency plays a pathogenic role in diabetic cardiomyopathy.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Jan;102:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.11.013. Epub 2016 Nov 30. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27913284 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles of immunoproteasomes beyond MHC class I antigen processing.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(15):2543-58. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0938-0. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22382925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Proteasome Subunit Low Molecular Weight Protein (LMP)-2 Is Required to Induce Active Remodeling in Adult Rat Ventricular Cardiomyocytes.Med Sci (Basel). 2020 May 1;8(2):21. doi: 10.3390/medsci8020021. Med Sci (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32370048 Free PMC article.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning confers late protection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by upregulating interleukin-10.Basic Res Cardiol. 2012 Jul;107(4):277. doi: 10.1007/s00395-012-0277-1. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Basic Res Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22752341 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of CacyBP/SIP protein, β-catenin, and immunoproteasome subunit LMP7 in the heart of rats with hypertension of different etiology.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Nov;243(15-16):1199-1206. doi: 10.1177/1535370218815435. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 30472885 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modification of cardiac proteasomes: functional delineation enabled by proteomics.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jul;303(1):H9-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00189.2012. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22523251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, Levy D. The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22:6A–13A. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am J Cardiol. 1974;34:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Jackson CV, McGrath GM, Tahiliani AG, Vadlamudi RV, McNeill JH. A functional and ultrastructural analysis of experimental diabetic rat myocardium. Manifestation of a cardiomyopathy. Diabetes. 1985;34:876–883. - PubMed
-
- Aneja A, Tang WH, Bansilal S, Garcia MJ, Farkouh ME. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: insights into pathogenesis, diagnostic challenges, and therapeutic options. Am J Med. 2008;121:748–57. - PubMed
-
- Kettelhut IC, Pepato MT, Migliorini RH, Medina R, Goldberg AL. Regulation of different proteolytic pathways in skeletal muscle in fasting and diabetes mellitus. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994;27:981–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

