Dopamine and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 in the kidney: role in blood pressure regulation
- PMID: 20153824
- PMCID: PMC2892632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.02.004
Dopamine and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 in the kidney: role in blood pressure regulation
Abstract
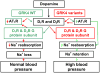
Complex interactions between genes and environment result in a sodium-induced elevation in blood pressure (salt sensitivity) and/or hypertension that lead to significant morbidity and mortality affecting up to 25% of the middle-aged adult population worldwide. Determining the etiology of genetic and/or environmentally-induced high blood pressure has been difficult because of the many interacting systems involved. Two main pathways have been implicated as principal determinants of blood pressure since they are located in the kidney (the key organ responsible for blood pressure regulation), and have profound effects on sodium balance: the dopaminergic and renin-angiotensin systems. These systems counteract or modulate each other, in concert with a host of intracellular second messenger pathways to regulate sodium and water balance. In particular, the G protein-coupled receptor kinase type 4 (GRK4) appears to play a key role in regulating dopaminergic-mediated natriuresis. Constitutively activated GRK4 gene variants (R65L, A142V, and A486V), by themselves or by their interaction with other genes involved in blood pressure regulation, are associated with essential hypertension and/or salt-sensitive hypertension in several ethnic groups. GRK4γ 142Vtransgenic mice are hypertensive on normal salt intake while GRK4γ 486V transgenic mice develop hypertension only with an increase in salt intake. GRK4 gene variants have been shown to hyperphosphorylate, desensitize, and internalize two members of the dopamine receptor family, the D(1) (D(1)R) and D(3) (D(3)R) dopamine receptors, but also increase the expression of a key receptor of the renin-angiotensin system, the angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT(1)R). Knowledge of the numerous blood pressure regulatory pathways involving angiotensin and dopamine may provide new therapeutic approaches to the pharmacological regulation of sodium excretion and ultimately blood pressure control.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dopamine Receptor D1R and D3R and GRK4 Interaction in Hypertension.Yale J Biol Med. 2023 Mar 31;96(1):95-105. doi: 10.59249/MKRR9549. eCollection 2023 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37009199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of GRK4 in the regulation of arterial AT1 receptor in hypertension.Hypertension. 2014 Feb;63(2):289-96. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.01766. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24218433 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive insights in GRK4 and hypertension: From mechanisms to potential therapeutics.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Nov;239:108194. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108194. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35487286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of GRK4 in the regulation of the renal ETB receptor in hypertension.FASEB J. 2020 Sep;34(9):11594-11604. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902552R. Epub 2020 Jul 20. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32687659 Free PMC article.
-
[G protein kinase 4gammaA142V overexpression induced hypertension by downregulating D1 receptors in transgenic mice].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2006 May;34(5):411-4. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16776954 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Structure and Function of the Hypertension Variant A486V of G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 4.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 14;290(33):20360-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.648907. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26134571 Free PMC article.
-
A linear relationship between the ex-vivo sodium mediated expression of two sodium regulatory pathways as a surrogate marker of salt sensitivity of blood pressure in exfoliated human renal proximal tubule cells: the virtual renal biopsy.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Jun 5;421:236-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.02.021. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23454474 Free PMC article.
-
Deficient dopamine D2 receptor function causes renal inflammation independently of high blood pressure.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038745. Epub 2012 Jun 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22719934 Free PMC article.
-
The dopamine D3 receptor knockout mouse mimics aging-related changes in autonomic function and cardiac fibrosis.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 30;8(8):e74116. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074116. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023697 Free PMC article.
-
The connection between GRKs and various signaling pathways involved in diabetic nephropathy.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Jul;39(7):7717-26. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1608-x. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22350265 Review.
References
-
- Hussain T, Lokhandwala MF. Renal dopamine receptors and hypertension. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2003;228:134–42. - PubMed
-
- Carey RM, VanLoon GR, Baines AD, Ortt EM. Decreased plasma and urinary dopamine during dietary sodium depletion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981;52:903–9. - PubMed
-
- Maurel A, Spreux-Varoquaux O, Amenta F, Tayebati SK, Tomassoni D, Seguelas MH, Parini A, Pizzinat N. Vesicular monoamine transporter 1 mediates dopamine secretion in rat proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292:F1592–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

