High temperature requirement A3 (HtrA3) promotes etoposide- and cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cell lines
- PMID: 20154083
- PMCID: PMC2852939
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.097790
High temperature requirement A3 (HtrA3) promotes etoposide- and cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cell lines
Abstract
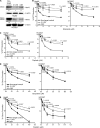
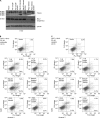
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Here we show for the first time that HtrA3 is a mitochondrial stress-response factor that promotes cytotoxicity to etoposide and cisplatin in lung cancer cell lines. Exogenous expression of wild type HtrA3 domain variants significantly attenuated cell survival with etoposide and cisplatin treatment in lung cancer cell lines H157 and A549 compared with expression of protease inactive mutants (S305A) or vector control. Conversely, HtrA3 suppression promoted cell survival with etoposide and cisplatin treatment in lung cancer cell lines Hop62 and HCC827. Survival was attenuated by re-expression of wild type HtrA3 variants during treatment but not by protease inactive mutants or vector control. HtrA3 also co-fractionated and co-localized with mitochondrial markers with both endogenous and exogenous expression in normal lung and lung cancer cell lines but was translocated from mitochondria following etoposide treatment. Moreover, HtrA3 translocation from mitochondria correlated with an increase in cell death that was attenuated by either HtrA3 suppression or Bcl-2 overexpression. Taken together, these results suggest that HtrA3 may be a previously uncharacterized mitochondrial cell death effector whose serine protease function may be crucial to modulating etoposide- and cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cell lines.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Methylation induced gene silencing of HtrA3 in smoking-related lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 15;16(2):398-409. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1677. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20068077
-
The HtrA3 protease promotes drug-induced death of lung cancer cells by cleavage of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP).FEBS J. 2019 Nov;286(22):4579-4596. doi: 10.1111/febs.14977. Epub 2019 Jul 11. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 31260151
-
Antagonism between HTRA3 and TGFβ1 Contributes to Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 1;79(11):2853-2864. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2507. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30940659
-
High temperature requirement A3 (HTRA3) expression predicts postoperative recurrence and survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40725-40734. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9173. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27166271 Free PMC article.
-
High-temperature requirement factor A3 (Htra3): a novel serine protease and its potential role in ovarian function and ovarian cancers.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Oct 7;327(1-2):13-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20540986 Review.
Cited by
-
Human high temperature requirement serine protease A1 (HTRA1) degrades tau protein aggregates.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 15;287(25):20931-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.316232. Epub 2012 Apr 25. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22535953 Free PMC article.
-
Quinacrine Induces Nucleolar Stress in Treatment-Refractory Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 16;13(18):4645. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184645. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572872 Free PMC article.
-
HtrA3 Is Downregulated in Cancer Cell Lines and Significantly Reduced in Primary Serous and Granulosa Cell Ovarian Tumors.J Cancer. 2013;4(2):152-64. doi: 10.7150/jca.5702. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23412729 Free PMC article.
-
HtrA4 Protease Promotes Chemotherapeutic-Dependent Cancer Cell Death.Cells. 2019 Sep 20;8(10):1112. doi: 10.3390/cells8101112. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31546993 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of Human HtrA Family Proteases and Their Distinctive Physiological Roles and Unique Involvement in Diseases, Especially Cancer and Pregnancy Complications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 6;22(19):10756. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910756. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639128 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Hao Y., Xu J., Murray T., Thun M. J. (2008) CA-Cancer J. Clin. 58, 71–96 - PubMed
-
- Minna J. D., Schiller J. H. (2008) Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th Ed., McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York
-
- Ciombor K. K., Rocha Lima C. M. (2006) Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 7, 59–68 - PubMed
-
- Ferraldeschi R., Baka S., Jyoti B., Faivre-Finn C., Thatcher N., Lorigan P. (2007) Drugs 67, 2135–2152 - PubMed
-
- Fischer B., Arcaro A. (2008) Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 3, 40–61 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

