Role of Geobacter sulfurreducens outer surface c-type cytochromes in reduction of soil humic acid and anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate
- PMID: 20154112
- PMCID: PMC2849258
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02250-09
Role of Geobacter sulfurreducens outer surface c-type cytochromes in reduction of soil humic acid and anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate
Abstract
Deleting individual genes for outer surface c-type cytochromes in Geobacter sulfurreducens partially inhibited the reduction of humic substances and anthraquinone-2,6,-disulfonate. Complete inhibition was obtained only when five of these genes were simultaneously deleted, suggesting that diverse outer surface cytochromes can contribute to the reduction of humic substances and other extracellular quinones.
Figures
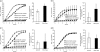


References
-
- Anderson, R. T., J. N. Rooney-Varga, C. V. Gaw, and D. R. Lovley. 1998. Anaerobic benzene oxidation in the Fe(III) reduction zone of petroleum-contaminated aquifers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32:1222-1229.
-
- Bhushan, B., A. Halasz, and J. Hawari. 2006. Effect of iron(III), humic acids and anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate on biodegradation of cyclic nitramines by Clostridium sp. EDB2. J. Appl. Microbiol. 100:555-563. - PubMed
-
- Bond, D. R., and D. R. Lovley. 2002. Reduction of Fe(III) oxide by methanogens in the presence and absence of extracellular quinones. Environ. Microbiol. 4:115-124. - PubMed
-
- Bradley, P. M., and F. H. Chapelle. 1996. Anaerobic mineralization of vinyl chloride in Fe(III)-reducing, aquifer sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30:2084-2086.
-
- Cervantes, F. J., F. A. de Bok, T. Duong-Dac, A. J. Stams, G. Lettinga, and J. A. Field. 2002. Reduction of humic substances by halorespiring, sulphate-reducing and methanogenic microorganisms. Environ. Microbiol. 4:51-57. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

