Proteinase-activated receptor-2 up-regulation by Fcgamma-receptor activation in human neutrophils
- PMID: 20154268
- PMCID: PMC2881300
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-146167
Proteinase-activated receptor-2 up-regulation by Fcgamma-receptor activation in human neutrophils
Abstract
We shed new light on the expression and function of the proteinase-activated receptor (PAR) family, associated with inflammation and hyperalgesia, in human granulocytes. Resting cells expressed constitutive levels of PAR-2 and PAR-3 mRNA but not PAR-1 or PAR-4. Based on flow cytometry, stimulation with opsonized bacteria (Bop) specifically up-regulated cell surface expression of PAR-2 in a concentration-dependent and time-dependent manner, independent of transcription or de novo protein synthesis. Primary granules were identified as a source of preformed PAR-2 that can readily be mobilized at the surface on fusion with the plasma membrane. Cellular response to PAR-2 activation, measured as changes in intracellular calcium concentration, was enhanced in PAR-2 up-regulated cells. Increase of cell-surface PAR-2 and of cell responsiveness were dependent specifically on the engagement of immunoglobulin (Ig)-binding receptors. Together, our results reveal that mobilization of intracellular granules, in response to Ig-receptor activation, up-regulates PAR-2 surface expression and makes neutrophils more responsive to proteinase activity. This enhanced response to PAR-2 activation indicates that molecular communication between pain and inflammation may be more important than previously believed.
Figures
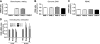
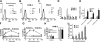
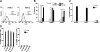
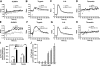
References
-
- Coughlin S. R. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature. 2000;407:258–264. - PubMed
-
- Ossovskaya V. S., Bunnett N. W. Protease-activated receptors: contribution to physiology and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:579–621. - PubMed
-
- Uehara A., Sugawara Y., Sasano T., Takada H., Sugawara S. Proinflammatory cytokines induce proteinase 3 as membrane-bound and secretory forms in human oral epithelial cells and antibodies to proteinase 3 activate the cells through protease-activated receptor-2. J Immunol. 2004;173:4179–4189. - PubMed
-
- Sekiguchi F. Development of agonists/antagonists for protease-activated receptors (PARs) and the possible therapeutic application to gastrointestinal diseases. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2005;125:491–498. - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi-Matsui M., Zheng Y. W., Sulciner D. J., Weiss E. J., Ludeman M. J., Coughlin S. R. PAR3 is a cofactor for PAR4 activation by thrombin. Nature. 2000;404:609–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

