C-C chemokine receptor 1 expression in human hematolymphoid neoplasia
- PMID: 20154287
- PMCID: PMC4305436
- DOI: 10.1309/AJCP1TA3FLOQTMHF
C-C chemokine receptor 1 expression in human hematolymphoid neoplasia
Abstract
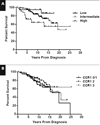
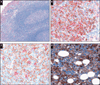
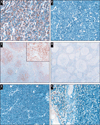
Chemokine receptor 1 (CCR1) is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds to members of the C-C chemokine family. Recently, CCL3 (MIP-1alpha), a high-affinity CCR1 ligand, was identified as part of a model that independently predicts survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). However, the role of chemokine signaling in the pathogenesis of human lymphomas is unclear. In normal human hematopoietic tissues, we found CCR1 expression in intraepithelial B cells of human tonsil and granulocytic/monocytic cells in the bone marrow. Immunohistochemical analysis of 944 cases of hematolymphoid neoplasia identified CCR1 expression in a subset of B- and T-cell lymphomas, plasma cell myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma. CCR1 expression correlated with the non-germinal center subtype of DLBCL but did not predict overall survival in follicular lymphoma. These data suggest that CCR1 may be useful for lymphoma classification and support a role for chemokine signaling in the pathogenesis of hematolymphoid neoplasia.
Figures


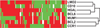
Similar articles
-
Distinct Chemokine Receptor Expression Profiles in De Novo DLBCL, Transformed Follicular Lymphoma, Richter's Trans-Formed DLBCL and Germinal Center B-Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 17;23(14):7874. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147874. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887224 Free PMC article.
-
MIP-1alpha utilizes both CCR1 and CCR5 to induce osteoclast formation and increase adhesion of myeloma cells to marrow stromal cells.Exp Hematol. 2005 Mar;33(3):272-8. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2004.11.015. Exp Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15730850
-
Clinical significance of chemokine receptor (CCR1, CCR2 and CXCR4) expression in human myeloma cells: the association with disease activity and survival.Haematologica. 2006 Feb;91(2):200-6. Haematologica. 2006. PMID: 16461304
-
Therapeutic potential of CCR1 antagonists for multiple myeloma.Future Med Chem. 2011 Nov;3(15):1889-908. doi: 10.4155/fmc.11.144. Future Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 22023033 Review.
-
CCR1 as a target for multiple myeloma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011 Sep;15(9):1037-47. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2011.586634. Epub 2011 May 24. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011. PMID: 21609295 Review.
Cited by
-
GWAS-identified CCR1 and IL10 loci contribute to M1 macrophage-predominant inflammation in Behçet's disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Jun 12;20(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1613-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29895319 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine Receptors CCR1 and CCR2 on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Newly Diagnosed Patients with the CD38-Positive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.J Clin Med. 2020 Jul 21;9(7):2312. doi: 10.3390/jcm9072312. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32708233 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-Chemokine CCL15 Affects the Adhesion and Migration of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells.Transfus Med Hemother. 2015 Jan;42(1):29-37. doi: 10.1159/000370168. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Transfus Med Hemother. 2015. PMID: 25960713 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte-endothelial cell interactions in vascular and tissue remodeling.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 7;14:1196033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1196033. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37483594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine-Directed Tumor Microenvironment Modulation in Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9804. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189804. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Rollins BJ. Inflammatory chemokines in cancer growth and progression. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:760–767. - PubMed
-
- Laurence AD. Location, movement and survival: the role of chemokines in haematopoiesis and malignancy. Br J Haematol. 2006;132:255–267. - PubMed
-
- Maurer M, von Stebut E. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:1882–1886. - PubMed
-
- Su SB, Mukaida N, Wang J, et al. Preparation of specific polyclonal antibodies to a C-C chemokine receptor, CCR1, and determination of CCR1 expression on various types of leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1996;60:658–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

