Role of amygdala and hippocampus in the neural circuit subserving conditioned defeat in Syrian hamsters
- PMID: 20154357
- PMCID: PMC2825696
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.1633710
Role of amygdala and hippocampus in the neural circuit subserving conditioned defeat in Syrian hamsters
Abstract
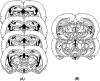
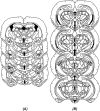
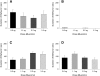
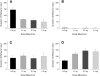
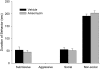
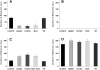
We examined the roles of the amygdala and hippocampus in the formation of emotionally relevant memories using an ethological model of conditioned fear termed conditioned defeat (CD). Temporary inactivation of the ventral, but not dorsal hippocampus (VH, DH, respectively) using muscimol disrupted the acquisition of CD, whereas pretraining VH infusions of anisomycin, a protein synthesis inhibitor, failed to block CD. To test for a functional connection between the VH and basolateral amygdala (BLA), we used a classic functional connectivity design wherein injections are made unilaterally in brain areas either on the same or opposite sides of the brain. A functional connection between the BLA and VH necessary for the acquisition of CD could not be found because unilateral inactivation of either BLA alone (but not either VH alone) was sufficient to disrupt CD. This finding suggested instead that there may be a critical functional connection between the left and right BLA. In our final experiment, we infused muscimol unilaterally in the BLA and assessed Fos immunoreactivity on the contralateral side following exposure to social defeat. Inactivation of either BLA significantly reduced defeat-induced Fos immunoreactivity in the contralateral BLA. These experiments demonstrate for the first time that whereas the VH is necessary for the acquisition of CD, it does not appear to mediate the plastic changes underlying CD. There also appears to be a critical interaction between the two BLAs such that bilateral activation of this brain area must occur in order to support fear learning in this model, a finding that is unprecedented to date.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The medial prefrontal cortex is both necessary and sufficient for the acquisition of conditioned defeat.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Feb;62(2):933-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.09.026. Epub 2011 Oct 8. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22001285 Free PMC article.
-
NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor in the basolateral amygdala is necessary for the acquisition of conditioned defeat in Syrian hamsters.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Feb 2;217(1):55-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.09.034. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 20933543 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of GABA(A) receptors in the amygdala blocks the acquisition and expression of conditioned defeat in Syrian hamsters.Brain Res. 2001 Nov 30;920(1-2):142-50. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03054-2. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11716820
-
Understanding contextual fear conditioning: insights from a two-process model.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004 Nov;28(7):675-85. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2004.09.004. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004. PMID: 15555677 Review.
-
Overlapping neurobiology of learned helplessness and conditioned defeat: implications for PTSD and mood disorders.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Feb;62(2):565-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.02.024. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21396383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone deacetylase and acetyltransferase inhibitors modulate behavioral responses to social stress.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017 Jan;75:100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.10.022. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017. PMID: 27810703 Free PMC article.
-
Social Dominance Modulates Stress-induced Neural Activity in Medial Prefrontal Cortex Projections to the Basolateral Amygdala.Neuroscience. 2018 Sep 15;388:274-283. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.07.042. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 30075245 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine in the nucleus accumbens modulates the memory of social defeat in Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus).Behav Brain Res. 2015 Jun 1;286:22-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.02.030. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25721736 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic cleavage of proBDNF into mature BDNF in the basolateral amygdala is necessary for defeat-induced social avoidance.Learn Mem. 2016 Mar 15;23(4):156-60. doi: 10.1101/lm.040253.115. Print 2016 Apr. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 26980783 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics reveals distinct neurochemical profiles associated with stress resilience.Neurobiol Stress. 2017 Aug 7;7:103-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2017.08.001. eCollection 2017 Dec. Neurobiol Stress. 2017. PMID: 28828396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amaral DG, Insausti R. Retrograde transport of D-[3H]-aspartate injected into the monkey amygdaloid complex. Exp Brain Res. 1992;88:375–388. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Rawlins JNP, McHugh SB, Deacon RMJ, Yee BK, Bast T, Zhang W-N, Pothuizen HHJ, Feldon J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus—memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J. The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats. Different anterograde amnesias of fear after tetrodotoxin inactivation and infusion of the GABAA agonist muscimol. Exp Brain Res. 2001;139:39–52. - PubMed
-
- Czerniawski J, Yoon T, Otto T. Dissociating space and trace in dorsal and ventral hippocampus. Hippocampus. 2009;19:20–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
