Assessment of the role of MAP kinase in mediating activity-dependent transcriptional activation of the immediate early gene Arc/Arg3.1 in the dentate gyrus in vivo
- PMID: 20154358
- PMCID: PMC2825695
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.1585910
Assessment of the role of MAP kinase in mediating activity-dependent transcriptional activation of the immediate early gene Arc/Arg3.1 in the dentate gyrus in vivo
Abstract
Different physiological and behavioral events activate transcription of Arc/Arg3.1 in neurons in vivo, but the signal transduction pathways that mediate induction in particular situations remain to be defined. Here, we explore the relationships between induction of Arc/Arg3.1 transcription in dentate granule cells in vivo and activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase as measured by extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation. We show that ERK1/2 phosphorylation is strongly induced in dentate granule cells within minutes after induction of perforant path long-term potentiation (LTP). Phospho-ERK staining appears in nuclei within minutes after stimulation commences, and ERK phosphorylation returns to control levels within 60 min. Electroconvulsive seizures, which strongly induce prolonged Arc/Arg3.1 transcription in dentate granule cells, induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in granule cells that returned to control levels within 30 min. Following 30, 60, and 120 min of exploration in a novel complex environment, Arc/Arg3.1 transcription was activated in many more granule cells than stained positively for p-ERK at all time points. Although Arc/Arg3.1 transcription was induced in most pyramidal neurons in CA1 following exploration, very few pyramidal neurons exhibited nuclear p-ERK1/2 staining. Local delivery of U0126 during the induction of perforant path LTP blocked transcriptional activation of Arc/Arg3.1 in a small region near the injection site and blocked Arc/Arg3.1 protein expression over a wider region. Our results indicate that activation of Arc/Arg3.1 transcription in dentate granule cells in vivo is mediated in part by MAP kinase activation, but other signaling pathways also contribute, especially in the case of Arc/Arg3.1 induction in response to experience.
Figures
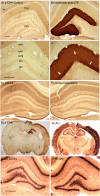



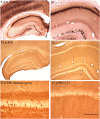
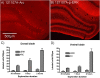


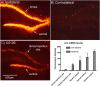
Similar articles
-
Actin polymerization and ERK phosphorylation are required for Arc/Arg3.1 mRNA targeting to activated synaptic sites on dendrites.J Neurosci. 2007 Aug 22;27(34):9054-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2410-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17715342 Free PMC article.
-
Novel translational control in Arc-dependent long term potentiation consolidation in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 13;284(46):31498-511. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056077. Epub 2009 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19755425 Free PMC article.
-
NAc Shell Arc/Arg3.1 Protein Mediates Reconsolidation of Morphine CPP by Increased GluR1 Cell Surface Expression: Activation of ERK-Coupled CREB is Required.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Mar 6;18(9):pyv030. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv030. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25746394 Free PMC article.
-
The immediate early gene arc/arg3.1: regulation, mechanisms, and function.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 12;28(46):11760-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3864-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19005037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of Arc in synaptic plasticity.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 May;77:3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 28890422 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-time imaging of Arc/Arg3.1 transcription ex vivo reveals input-specific immediate early gene dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Sep 20;119(38):e2123373119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2123373119. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36095210 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptically driven phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 is differentially regulated at active synapses versus dendrites and cell bodies by MAPK and PI3K/mTOR signaling pathways.Learn Mem. 2017 Jul 17;24(8):341-357. doi: 10.1101/lm.044974.117. Print 2017 Aug. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28716954 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of nuclear organization and dynamics on epigenetic regulation in the central nervous system: implications for neurological disease states.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Sep;1204 Suppl(Suppl):E20-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05718.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20840166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Convergence of nicotine-induced and auditory-evoked neural activity activates ERK in auditory cortex.Synapse. 2013 Aug;67(8):455-68. doi: 10.1002/syn.21647. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Synapse. 2013. PMID: 23401204 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling the MAPK/ERK dependent and independent activity regulated transcriptional programs in the murine hippocampus in vivo.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 28;7:45101. doi: 10.1038/srep45101. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28349920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chawla MK, Guzowski JF, Ramirez-Amaya V, Lipa P, Hoffman KL, Marriott LK, Worley PF, McNaughton BL, Barnes CA. Sparse, environmentally selective expression of Arc RNA in the upper blade of the rodent fascia dentata by brief spatial experience. Hippocampus. 2005;10:579–586. - PubMed
-
- Coogan AN, O'Leary DM, O'Connor JJ. P42/44 MAP kinase inhibitor PD98059 attenuates multiple forms of synaptic plasticity in rat dentate gyrus in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1999;81:103–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
