An insertion of intracisternal A-particle retrotransposon in a novel member of the phosphoglycerate mutase family in the lew allele of mutant mice
- PMID: 20154419
- PMCID: PMC3155949
- DOI: 10.1266/ggs.84.327
An insertion of intracisternal A-particle retrotransposon in a novel member of the phosphoglycerate mutase family in the lew allele of mutant mice
Abstract
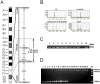
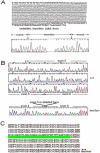
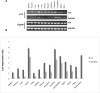
Intracisternal A-particle retrotransposons (IAPs) are known, moveable, retrovirus-like elements and are defective in envelope protein synthesis in the mouse genome. Insertion of IAP elements can either interupt or enhance gene function or expression. Using a mouse model called lethal wasting (lew), we recently identified the insertion of an IAP sequence in a gene, 9630033F20Rik, that contains domains involved in glycolysis. The expression pattern of the 9630033F20Rik gene between various normal and diseased tissues was determined by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. The effect of the insertion mutation in 9630033F20Rik on glycolysis in heart, muscle, and brain tissues was further investigated using oligonuleotide microarray analysis. Results indicated that the expression of 9630033F20Rik is ubiquitous and its signal is relatively higher in heart and brain tissues. The insertion caused the deletion of exon 5 and decreased expression of this gene in all the tissues studied in the lew mice. Changes in the expression levels of glycolytic genes mainly occured in muscle tissue, raising a possibility that 9630033F20Rik may function as one of the transcriptional regulators of glycolytic genes in skeletal muscle. However, considering the fact that a single nucleotide mutation in vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (VAMP1) has been reported as the causal gene for the lew mouse, how much of an impact the IAP insertion in the lew mouse phenotype has on glycolytic genes compared to the effect from the VAMP1 mutation responsible for the lew mouse phenotype should be further investigated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene network of a phosphoglycerate mutase in muscle wasting in mice.Cell Biol Int. 2015 Jun;39(6):666-77. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10437. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Cell Biol Int. 2015. PMID: 25644094
-
A null mutation in VAMP1/synaptobrevin is associated with neurological defects and prewean mortality in the lethal-wasting mouse mutant.Neurogenetics. 2007 Jan;8(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s10048-006-0068-7. Epub 2006 Nov 11. Neurogenetics. 2007. PMID: 17102983
-
Negative and positive effects of an IAP-LTR on nearby Pcdaalpha gene expression in the central nervous system and neuroblastoma cell lines.Gene. 2004 Aug 4;337:91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.04.011. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15276205
-
Insertion of an intracisternal A particle retrotransposon element in plasma membrane calcium ATPase 2 gene attenuates its expression and produces an ataxic phenotype in joggle mutant mice.Gene. 2008 Mar 31;411(1-2):94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.01.013. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Gene. 2008. PMID: 18280673
-
Molecular biology of type A endogenous retrovirus.Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990 Sep;63(2-3):77-90. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1990. PMID: 1710682 Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal maternal immune activation causes epigenetic differences in adolescent mouse brain.Transl Psychiatry. 2014 Sep 2;4(9):e434. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.80. Transl Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25180573 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse germ line mutations due to retrotransposon insertions.Mob DNA. 2019 Apr 13;10:15. doi: 10.1186/s13100-019-0157-4. eCollection 2019. Mob DNA. 2019. PMID: 31011371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Besse S, Allamand V, Vilquin JT, Li Z, Poirier C, Vignier N, Hori H, Guenet JL, Guicheney P. Spontaneous muscular dystrophy caused by a retrotransposal insertion in the mouse laminin alpha2 chain gene. Neuromuscul Disord. 2003;13:216–22. - PubMed
-
- Cao PR, Kim HJ, Lecker SH. Ubiquitin-protein ligases in muscle wasting. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:2088–97. - PubMed
-
- Comi GP, Fortunato F, Lucchiari S, Bordoni A, Prelle A, Jann S, Keller A, Ciscato P, Galbiati S, Chiveri L, Torrente Y, Scarlato G, Bresolin N. Beta-enolase deficiency, a new metabolic myopathy of distal glycolysis. Ann Neurol. 2001;50:202–7. - PubMed
-
- DiMauro S, Miranda AF, Khan S, Gitlin K, Friedman R. Human muscle phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency: newly discovered metabolic myopathy. Science. 1981;212:1277–9. - PubMed
-
- Emery AE. The muscular dystrophies. Lancet. 2002;359:687–95. - PubMed

