Innate immune lectins kill bacteria expressing blood group antigen
- PMID: 20154696
- PMCID: PMC2853181
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2103
Innate immune lectins kill bacteria expressing blood group antigen
Abstract
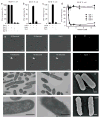
The expression of ABO(H) blood group antigens causes deletion of cells that generate self-specific antibodies to these antigens but this deletion limits adaptive immunity toward pathogens bearing cognate blood group antigens. To explore potential defense mechanisms against such pathogens, given these limitations in adaptive immunity, we screened for innate proteins that could recognize human blood group antigens. Here we report that two innate immune lectins, galectin-4 (Gal-4) and Gal-8, which are expressed in the intestinal tract, recognize and kill human blood group antigen-expressing Escherichia coli while failing to alter the viability of other E. coli strains or other Gram-negative or Gram-positive organisms both in vitro and in vivo. The killing activity of both Gal-4 and Gal-8 is mediated by their C-terminal domains, occurs rapidly and independently of complement and is accompanied by disruption of membrane integrity. These results demonstrate that innate defense lectins can provide immunity against pathogens that express blood group-like antigens on their surface.
Figures
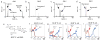
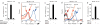

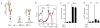
Comment in
-
A sweet target for innate immunity.Nat Med. 2010 Mar;16(3):263-4. doi: 10.1038/nm0310-263. Nat Med. 2010. PMID: 20208507 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yamamoto F, Clausen H, White T, Marken J, Hakomori S. Molecular genetic basis of the histo-blood group ABO system. Nature. 1990;345:229–33. - PubMed
-
- Figdor CG, van Kooyk Y, Adema GJ. C-type lectin receptors on dendritic cells and Langerhans cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:77–84. - PubMed
-
- van Kooyk Y, Rabinovich GA. Protein-glycan interactions in the control of innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:593–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

