The novel squamosamide derivative FLZ enhances BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling and inhibits neuronal apoptosis in APP/PS1 mice
- PMID: 20154710
- PMCID: PMC4002416
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.3
The novel squamosamide derivative FLZ enhances BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling and inhibits neuronal apoptosis in APP/PS1 mice
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to study the effects of compound FLZ, a novel cyclic derivative of squamosamide from Annona glabra, on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)/tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB)/cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) signaling and neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus of the amyloid precursor protein (APP)/presenilin-1 (PS1) double transgenic mice.
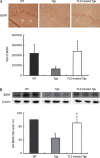
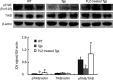
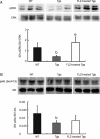
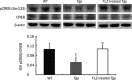
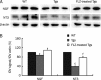
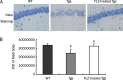
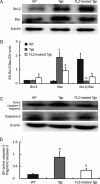
Methods: APP/PS1 mice at the age of 5 months and age-matched wild-type mice (WT) were intragastrically administered FLZ (150 mg/kg) or vehicle [0.05% carboxymethyl cellulose sodium (CMC-Na)] daily for 20 weeks. The levels of BDNF in the hippocampus of WT and APP/PS1 mice were then measured by immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. Neuronal apoptosis in mouse hippocampus was detected by Nissl staining. Expression of NGF, NT3, pTrkB (Tyr515)/TrkB, pAkt (Ser473)/Akt, pERK/ERK, pCREB (Ser133)/CREB, Bcl-2/Bax, and active caspase-3 fragment/caspase-3 in the hippocampus of WT and APP/PS1 mice was detected by Western blot analysis.
Results: Compared with vehicle-treated APP/PS1 mice, FLZ (150 mg/kg) significantly increased BDNF and NT3 expression in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice. In addition, FLZ promoted BDNF high-affinity receptor TrkB phosphorylation and activated its downstream ERK, thus increasing phosphorylation of CREB at Ser133 in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice. Moreover, FLZ showed neuroprotective effects on neuronal apoptosis by increasing the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and decreasing the active caspase-3 fragment/caspase-3 ratio in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice.
Conclusion: FLZ exerted neuroprotection at least partly through enhancing the BDNF/TrkB/CREB pathway and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis in APP/PS1 mice, which suggests that FLZ can be explored as a potential therapeutic agent in long-term Alzheimer's disease therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Scinto LF, Wu CK, Firla KM, Daffner KR, Saroff D, Geula C. Focal pathology in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus explains pupillary hypersensitivity in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1999;97:557–64. - PubMed
-
- Auld DS, Kornecook TJ, Bastianetto S, Quirion R. Alzheimer's disease and the basal forebrain cholinergic system: relations to beta-amyloid peptides, cognition, and treatment strategies. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:209–45. - PubMed
-
- Schliebs R, Arendt T. The significance of the cholinergic system in the brain during aging and in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm. 2006;113:1625–44. - PubMed
-
- Coleman PD, Yao PJ. Synaptic slaughter in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24:1023–7. - PubMed
-
- Okamura N, Suemoto T, Shiomitsu T, Suzuki M, Shimadzu H, Akatsu H, et al. A novel imaging probe for in vivo detection of neuritic and diffuse amyloid plaques in the brain. J Mol Neurosci. 2004;24:247–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

