Notch-1 stimulates survival of lung adenocarcinoma cells during hypoxia by activating the IGF-1R pathway
- PMID: 20154720
- PMCID: PMC2861728
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.7
Notch-1 stimulates survival of lung adenocarcinoma cells during hypoxia by activating the IGF-1R pathway
Abstract
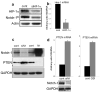
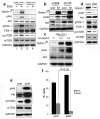
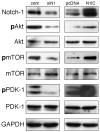
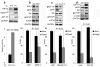
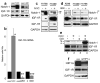
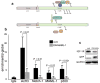
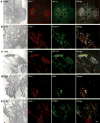
Hypoxic microenvironment supports cancer stem cell survival, causes poor response to anticancer therapy and tumor recurrence. Inhibition of Notch-1 signaling in adenocarcinoma of the lung (ACL) cells causes apoptosis specifically under hypoxia. Here, we found that Akt-1 activation is a key mediator of Notch-1 pro-survival effects under hypoxia. Notch-1 activates Akt-1 through repression of phosphatase and tensin (PTEN) homolog expression and induction of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R). The latter seems to be the major determinant of Akt-1 stimulation, as Notch-1 signaling affects Akt-1 activation in PTEN(-/-) ACL cells. Both downregulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) and dominant-negative IGF-1R sensitized ACL cells to gamma-secretase inhibitor (GSI)-induced apoptosis. Conversely, overexpression of IGF-1R protected ACL cells from GSI toxicity. Inhibition of Notch-1 caused reduced IGF-1R expression, whereas forced Notch-1 expression yielded opposite effects. Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments suggested Notch-1 direct regulation of the IGF-1R promoter. Experiments in which human ACL cells were injected in mice confirmed elevated and specific co-expression of Notch-1(IC), IGF-1R and pAkt-1 in hypoxic tumor areas. Our data provide a mechanistic explanation for Notch-1-mediated pro-survival function in hypoxic ACL tumor microenvironment. The results identify additional targets that may synergize with Notch-1 inhibition for ACL treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Notch1 receptor regulates AKT protein activation loop (Thr308) dephosphorylation through modulation of the PP2A phosphatase in phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-null T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 2;288(31):22836-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.451625. Epub 2013 Jun 20. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23788636 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased IGF type 1 receptor signaling in mammary epithelium during pregnancy leads to reduced proliferation, alveolar differentiation, and expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2.Endocrinology. 2011 Aug;152(8):3233-45. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1296. Epub 2011 May 31. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21628386 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen concentration determines the biological effects of NOTCH-1 signaling in adenocarcinoma of the lung.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 1;67(17):7954-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1229. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17804701
-
Opposite effects of Notch-1 and Notch-2 on mesothelioma cell survival under hypoxia are exerted through the Akt pathway.Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 1;68(23):9678-85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0969. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19047145
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
Cited by
-
Alveolar type II cells possess the capability of initiating lung tumor development.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053817. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23285300 Free PMC article.
-
Delta-tocotrienol suppresses Notch-1 pathway by upregulating miR-34a in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2012 Dec 1;131(11):2668-77. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27549. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22438124 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular and Cellular Strategies of Glioblastoma and Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Conferring Radioresistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 5;23(21):13577. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113577. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between the upregulation of Notch1 signaling and the clinical characteristics of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma in East Asia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Jan 3;19:5. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0723-8. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 30622441 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct molecular etiologies of male and female hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2019 Oct 15;19(1):951. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6167-2. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31615477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R, Hongo A, Rubini M, Prisco M, Valentinis B. The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1332:F105–F126. - PubMed
-
- Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F. Stimulation of Glucose Transport by Hypoxia: Signals and Mechanisms. News Physiol Sci. 1999;14:105–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

