tRNA nucleotidyltransferases: ancient catalysts with an unusual mechanism of polymerization
- PMID: 20155482
- PMCID: PMC11115931
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0271-4
tRNA nucleotidyltransferases: ancient catalysts with an unusual mechanism of polymerization
Abstract
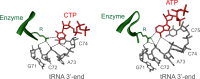
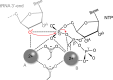
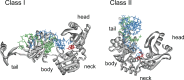
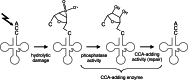
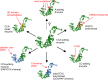
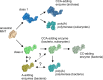
RNA polymerases are important enzymes involved in the realization of the genetic information encoded in the genome. Thereby, DNA sequences are used as templates to synthesize all types of RNA. Besides these classical polymerases, there exists another group of RNA polymerizing enzymes that do not depend on nucleic acid templates. Among those, tRNA nucleotidyltransferases show remarkable and unique features. These enzymes add the nucleotide triplet C-C-A to the 3'-end of tRNAs at an astonishing fidelity and are described as "CCA-adding enzymes". During this incorporation of exactly three nucleotides, the enzymes have to switch from CTP to ATP specificity. How these tasks are fulfilled by rather simple and small enzymes without the help of a nucleic acid template is a fascinating research area. Surprising results of biochemical and structural studies allow scientists to understand at least some of the mechanistic principles of the unique polymerization mode of these highly unusual enzymes.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

