Surgical management of severe scoliosis with high risk pulmonary dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: patient function, quality of life and satisfaction
- PMID: 20155495
- PMCID: PMC2903179
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-010-0957-0
Surgical management of severe scoliosis with high risk pulmonary dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: patient function, quality of life and satisfaction
Abstract
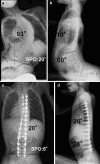
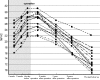
In a previous study, the authors reported the clinical and radiological results of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) scoliosis surgery in 14 patients with a low FVC of <30%. The purpose of this study was to determine if surgery improved function and QOL in these patients. Furthermore, the authors assessed the patients' and parents' satisfaction. %FVC increased in all patients after preoperative inspiratory muscle training. Scoliosis surgery in this group of patients presented no increased risk of major complications. All-screw constructions and fusion offered the ability to correct spinal deformity in the coronal and pelvic obliquity initially, intermediate and long-term. All patients were encouraged to continue inspiratory muscle training after surgery. The mean rate of %FVC decline after surgery was 3.6% per year. Most patients and parents believed scoliosis surgery improved their function, sitting balance and quality of life even though patients were at high risk for major complications. Their satisfaction was also high.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surgical correction of spinal deformity in patients with congenital muscular dystrophy.J Orthop Sci. 2010 Jul;15(4):493-501. doi: 10.1007/s00776-010-1486-9. Epub 2010 Aug 19. J Orthop Sci. 2010. PMID: 20721717
-
Surgical management of severe scoliosis with high-risk pulmonary dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Int Orthop. 2010 Mar;34(3):401-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-009-0764-7. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Int Orthop. 2010. PMID: 19340426 Free PMC article.
-
Pedicle screw-only constructs with lumbar or pelvic fixation for spinal stabilization in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009 Aug;22(6):428-33. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0b013e3181872d74. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009. PMID: 19652570
-
Survival of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who underwent spinal deformity correction.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2024 Feb;66(2):187-194. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15711. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37482906 Review.
-
[Characteristics in the treatment of scoliosis in muscular diseases].Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1997 Mar-Apr;135(2):95-105. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1039563. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1997. PMID: 9214180 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Screw augmentation for spinopelvic fixation in neuromuscular spine deformities: technical note.Eur Spine J. 2015 Nov;24(11):2580-7. doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-4155-z. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Eur Spine J. 2015. PMID: 26261012
-
Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 2: respiratory, cardiac, bone health, and orthopaedic management.Lancet Neurol. 2018 Apr;17(4):347-361. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30025-5. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Lancet Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29395990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Current care strategies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy].Orthopade. 2014 Jul;43(7):636-42. doi: 10.1007/s00132-013-2217-7. Orthopade. 2014. PMID: 24906240 Review. German.
-
Assessment and management of respiratory function in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: current and emerging options.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015 Sep 28;11:1475-88. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S55889. eCollection 2015. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015. PMID: 26451113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: the state of the art.Neurol Sci. 2018 Nov;39(11):1837-1845. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3555-3. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30218397 Review.
References
-
- Bonnett C, Brown JC, Perry J, Nickel VL, Walinski T, Brooks L, Hoffer M, Stiles C, Brooks R. Evolution of treatment of paralytic scoliosis at Ranchos Los Amigos Hospital. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57:206–215. - PubMed
-
- Bridwell KH, Baldus C, Iffrig TM. Process measures and patient/parent evaluation of surgical management of spinal deformities in patients with progressive flaccid neuromuscular scoliosis (Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy) Spine. 1999;24:1300–1309. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199907010-00006. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

