Achiral and chiral separations using MEKC, polyelectrolyte multilayer coatings, and mixed mode separation techniques with molecular micelles
- PMID: 20155738
- PMCID: PMC4197839
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.200900508
Achiral and chiral separations using MEKC, polyelectrolyte multilayer coatings, and mixed mode separation techniques with molecular micelles
Abstract
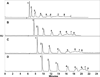
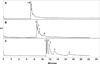
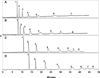
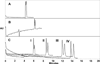
Mixed mode (MM) separation using a combination of MEKC and polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM) coatings is herein reported for the separation of achiral and chiral analytes. Many analytes are difficult to separate by MEKC and PEM coatings alone. Therefore, the implementation of a MM separation provides several advantages for overcoming the limitations of these well-established methods. In this study, it was observed that achiral separations using MEKC and PEM coatings individually resulted in partial resolution of eight very similar aryl ketones when the molecular micelle (sodium poly(N-undecanoyl-L-glycinate)) concentration was varied from 0.25 to 1.00% w/v and the bilayer number varied from 2 to 4. However, when MM separation was introduced, baseline resolution was achieved for all eight analytes. In the case of chiral separations, temazepam, aminoglutethimide, benzoin, benzoin methyl ether, and coumachlor were separated using the three separation techniques. For chiral separations, the chiral molecular micelle, sodium poly(N-undecanoyl-L-leucylvalinate), was employed at concentrations of 0.25-1.50% w/v for both MEKC and PEM coatings. Overall, the results revealed partial separation with MEKC and PEM coatings individually. However, MM separation enabled baseline separation of each chiral mixture. The separation of achiral and chiral compounds from different compound classes demonstrates the versatility of this MM approach.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of poly(sodium oleyl-L-leucylvalinate) surfactant for the separation of chiral compounds in micellar electrokinetic chromatography.Electrophoresis. 2003 Sep;24(17):2940-7. doi: 10.1002/elps.200305521. Electrophoresis. 2003. PMID: 12973797
-
Enantioselectivity of alcohol-modified polymeric surfactants in micellar electrokinetic chromatography.Electrophoresis. 2003 Aug;24(15):2499-507. doi: 10.1002/elps.200305507. Electrophoresis. 2003. PMID: 12900861
-
Protein separations using polyelectrolyte multilayer coatings with molecular micelles in open tubular capillary electrochromatography.Electrophoresis. 2008 Feb;29(4):889-900. doi: 10.1002/elps.200700634. Electrophoresis. 2008. PMID: 18219648
-
Enantiomer separation of drugs by micellar electrokinetic chromatography using chiral surfactants.J Chromatogr A. 2000 Apr 14;875(1-2):163-78. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(99)01167-x. J Chromatogr A. 2000. PMID: 10839143 Review.
-
Micellar electrokinetic chromatography for high-performance analytical separation.Chem Rec. 2008;8(5):291-301. doi: 10.1002/tcr.20156. Chem Rec. 2008. PMID: 18956478 Review.
References
-
- Rivi SA, Akbay C, Shamsi SA. Electrophoresis. 2004;25:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Caner H, Groner E, Levy L, Agranat I. Drug Discovery Today. 2004;9:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Terabe S, Otsuka K, Ichikawa K, Tsuchiya A, Ando T. Anal. Chem. 1984;56:111–113.
-
- Stenson C. S. Chem. Eng. News. 2001 May 14;:45.
-
- Terabe S, Shibata M, Miyashita Y. J.Chromatogr. A. 1989;480:403–411.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

