A novel microRNA and transcription factor mediated regulatory network in schizophrenia
- PMID: 20156358
- PMCID: PMC2834616
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-10
A novel microRNA and transcription factor mediated regulatory network in schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder with molecular mechanisms that have yet to be elucidated. Previous studies have suggested that changes in gene expression may play an important role in the etiology of schizophrenia, and that microRNAs (miRNAs) and transcription factors (TFs) are primary regulators of this gene expression. So far, several miRNA-TF mediated regulatory modules have been verified. We hypothesized that miRNAs and TFs might play combinatory regulatory roles for schizophrenia genes and, thus, explored miRNA-TF regulatory networks in schizophrenia.
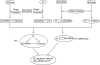
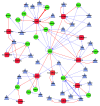
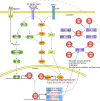
Results: We identified 32 feed-forward loops (FFLs) among our compiled schizophrenia-related miRNAs, TFs and genes. Our evaluation revealed that these observed FFLs were significantly enriched in schizophrenia genes. By converging the FFLs and mutual feedback loops, we constructed a novel miRNA-TF regulatory network for schizophrenia. Our analysis revealed EGR3 and hsa-miR-195 were core regulators in this regulatory network. We next proposed a model highlighting EGR3 and miRNAs involved in signaling pathways and regulatory networks in the nervous system. Finally, we suggested several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located on miRNAs, their target sites, and TFBSs, which may have an effect in schizophrenia gene regulation.
Conclusions: This study provides many insights on the regulatory mechanisms of genes involved in schizophrenia. It represents the first investigation of a miRNA-TF regulatory network for a complex disease, as demonstrated in schizophrenia.
Figures

References
-
- Maycox PR, Kelly F, Taylor A, Bates S, Reid J, Logendra R, Barnes MR, Larminie C, Jones N, Lennon M. Analysis of gene expression in two large schizophrenia cohorts identifies multiple changes associated with nerve terminal function. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14:1083–1094. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.18. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

