Regulated exocytosis in astrocytic signal integration
- PMID: 20156504
- PMCID: PMC2892557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2010.02.007
Regulated exocytosis in astrocytic signal integration
Abstract
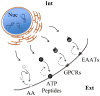
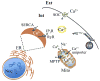
Astrocytes can be considered as signal integrators in central nervous system activity. These glial cells can respond to signals from the heterocellular milieu of the brain and subsequently release various molecules to signal to themselves and/or other neighboring neural cells. An important functional module that enables signal integration in astrocytes is exocytosis, a Ca(2+)-dependent process consisting of vesicular fusion to the plasma membrane. Astrocytes utilize regulated exocytosis to release various signaling molecules stored in the vesicular lumen. Here we review the properties of exocytotic release of three classes of gliotransmitters: (i) amino acids, (ii) nucleotides and (iii) peptides. Vesicles may carry not only lumenal cargo, but also membrane-associated molecules. Therefore, we also discuss exocytosis as a delivery mechanism for transporters and receptors to the plasma membrane, where these proteins are involved in astrocytic intercellular signaling.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson CM, Nedergaard M. Astrocyte-mediated control of cerebral microcirculation. Trends Neurosci. 2003;26:340–344. author reply 344-345. - PubMed
-
- Anlauf E, Derouiche A. Astrocytic exocytosis vesicles and glutamate: a high-resolution immunofluorescence study. Glia. 2005;49:96–106. - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Glutamate-dependent astrocyte modulation of synaptic transmission between cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1998b;10:2129–2142. - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:208–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

