Analysis of postural sway in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus: effects of shunt implantation
- PMID: 20156726
- PMCID: PMC3521352
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-s4-53
Analysis of postural sway in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus: effects of shunt implantation
Abstract
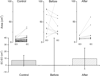
Poor postural balance is one of the major risk factors for falling in normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). Postural instability in the clinic is commonly assessed based upon force platform posturography. In this study we focused on the identification of changes in sway characteristics while standing quiet in patients with NPH before and after shunt implantation. Postural sway area and sway radius were analyzed in a group of 9 patients and 46 controls of both genders. Subject's spontaneous sway was recorded while standing quiet on a force platform for 30-60 s, with eyes open and then closed. Both analyzed sway descriptors identified between-group differences and also an effect of shunt implantation in the NPH group. Sway radius and sway area in patients exhibited very high values compared with those in the control group. Importantly, the effect of eyesight in patients was not observed before shunt implantation and reappeared after the surgical treatment. The study documents that static force platform posturography may be a reliable measure of postural control improvement due to shunt surgery.
Figures





References
-
- Massion J, Duffose M. Coordination between posture and movement: why and how. News Physiol Sci. 1988;3:88–93.
-
- Winter DA. ABC (Anatomy, Biomechanics and Control) of balance during standing and walking. Waterloo, Ontario. 1995. pp. 1–55.
-
- Collins JJ, De Luca CJ. Open-loop and closed-loop control of posture: A random walk analysis of center of pressure trajectories. Exp Brain Res. 1993;95(2):308–18. - PubMed
-
- Eng J, Winter DA. Estimation of the horizontal displacement of the total body centre of mass: considerations during standing activities. Gait Posture. 1993;1:141–44. doi: 10.1016/0966-6362(93)90055-6. - DOI
-
- Riach CL, Starkes JL. Stability limits of quiet standing postural control in children and adults. Gait Posture. 1993;1:105–11. doi: 10.1016/0966-6362(93)90021-R. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
