Influence of proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphism on childhood obesity
- PMID: 20156727
- PMCID: PMC3521345
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-s4-59
Influence of proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphism on childhood obesity
Abstract
Background: Obesity development is a complex process which can be influenced by genetic predisposition modified by environmental factors. Nowadays, the problem of overweight and obesity, including related complications, occurs in increasingly younger children. Thus, there is a need for new genetic markers of increased risk of excessive body mass.
Objective: The aim of the present study was to examine the relation between polymorphisms located in promoter regions of IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha genes and obesity development in children. Fifty obese and 55 normal weighing children were enrolled into the study. Genetic examination was performed using PCR-RFLP technique.
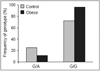
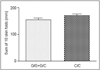
Results: We found a relation between G174C polymorphism in IL-6 gene and G308A in TNF-alpha gene with the occurrence of obesity. Allele A in G308A was more frequent in the obese group than in the control one (P=0.04). The presence of allele C in promoter region of IL-6 gene was more frequent in obese children and connected with a statistically significant increase in the sum of 10 skin fold thickness measurements (P=0.03).
Conclusions: The polymorphism C3954T in IL-1beta gene showed no such relation. The examined polymorphisms of proinflammatory cytokines play a role in the regulation of body mass through their influence on metabolism and energetic homeostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of interleukin-6 and G174C polymorphism in IL-6 gene on obesity and energy balance.Eur J Med Res. 2010 Nov 4;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):123-7. doi: 10.1186/2047-783x-15-s2-123. Eur J Med Res. 2010. PMID: 21147639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoter polymorphisms in IL-6 gene influence pro-inflammatory cytokines for the risk of osteoarthritis.Cytokine. 2020 Mar;127:154985. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.154985. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31951965
-
Association between interleukin-6 polymorphism and age-at-onset of type 1 diabetes. Epistatic influences of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta polymorphisms.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2005 Dec;16(4):277-81. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2005. PMID: 16464741
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β gene polymorphisms and risk of brain abscess in North Indian population.Cytokine. 2015 Sep;75(1):159-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.07.009. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26187330
-
An association study of inflammatory cytokine gene polymorphisms in Fabry disease.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006 Dec;17(4):271-5. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006. PMID: 17353161
Cited by
-
The role of IL-6 572 C/G, 190 C/T, and 174 G/C gene polymorphisms in children's obesity.Eur J Pediatr. 2014 Oct;173(10):1285-96. doi: 10.1007/s00431-014-2315-5. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Eur J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24740880
-
Influence of Interleukin-6 (174G/C) Gene Polymorphism on Obesity in Egyptian Children.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Oct 17;5(7):831-835. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.175. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29362605 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics, epigenetics and transgenerational transmission of obesity in children.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 14;13:1006008. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1006008. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36452324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of interleukin-6 and G174C polymorphism in IL-6 gene on obesity and energy balance.Eur J Med Res. 2010 Nov 4;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):123-7. doi: 10.1186/2047-783x-15-s2-123. Eur J Med Res. 2010. PMID: 21147639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between -174G>C polymorphism in the IL-6 promoter region and the risk of obesity: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(33):e11773. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011773. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30113463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allison DB. The hetitability of body mass index among an international sample of monozygotic twins reared apart. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996;20:501–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical