Tobacco abuse and physical activity among medical students
- PMID: 20156733
- PMCID: PMC3521348
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-s4-86
Tobacco abuse and physical activity among medical students
Abstract
Objective: This lifestyle is mainly determined during childhood and connected with poor public prophylactic health policy. The aim of this study was to estimate physical activity and level of tobacco abuse, as well as knowledge about health behaviours, among medical students.
Methods: Questionnaires were completed by Polish (243) and foreign medical students (80).
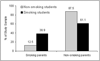
Results: It was stated that about 20% of the students smoked cigarettes. Female students from Norway took up smoking significantly more often than other participants, whereas there were more smokers among those from Poland. There was a significantly larger percentage of smoking males from Norway than among male Polish students. The same students presented a low level of physical activity. The smallest level of physical activity was characteristic of the Polish women.
Conclusion: This situation requires an intensification of activities aimed at supporting pro-health lifestyles and the elimination of unfavourable effects, especially among medical students.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Attitudes and behaviour concerning cigarette smoking among the students of the first year at the Health Department].Przegl Lek. 2006;63(10):1041-4. Przegl Lek. 2006. PMID: 17288211 Polish.
-
[Opinion of students of the Medical Department of Wroclaw Medical University on the subject of the fight against tobacco addiction].Przegl Lek. 2008;65(10):645-6. Przegl Lek. 2008. PMID: 19189569 Polish.
-
[The phenomenon of spreading smoking cigarettes among the first year course students in the Medical Academy].Przegl Lek. 2006;63(10):1031-7. Przegl Lek. 2006. PMID: 17288209 Polish.
-
[Tobacco smoking among students].Przegl Lek. 2006;63(10):1038-40. Przegl Lek. 2006. PMID: 17288210 Polish.
-
Education program about tobacco for medical students.Przegl Lek. 2005;62(10):1148-50. Przegl Lek. 2005. PMID: 16521976 Review.
Cited by
-
Health behaviors, care needs and attitudes towards self-prescription: a cross-sectional survey among Dutch medical students.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028038. Epub 2011 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22132202 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette, waterpipe and e-cigarette use among an international sample of medical students. Cross-sectional multicenter study in Germany and Hungary.BMC Public Health. 2018 May 3;18(1):591. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5494-6. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29724200 Free PMC article.
-
Medical students' health behaviour and self-reported mental health status by their country of origin: a cross-sectional study.BMC Psychiatry. 2016 May 28;16:171. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-0884-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27236478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woynarowska B, Malkowska-Szkutnik A, Mazur J. Subjective health of adolescents aged 11-15 years in Poland and other countries of the European Union. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2008;12:559–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
