Association between metabolic disturbances and G-174C polymorphism of interleukin-6 gene in obese children
- PMID: 20156756
- PMCID: PMC3521324
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-s4-196
Association between metabolic disturbances and G-174C polymorphism of interleukin-6 gene in obese children
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the study was to investigate whether the G-174C polymorphism of the IL-6 gene is related to obesity and the incidence of the metabolic syndrome (MetS) according to IDF definition in children.
Materials and methods: The examined group included 124 obese children with BMI > or = 2 SDS, and the control group consisted of 56 non-obese children with BMI <1.0 SDS. Polymorphism identification was performed in total genomic DNA using PCR-RFLP method.
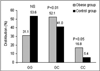
Results: In the obese children, carriers of C allele in homozygotic and heterozygotic genotypes were more frequent than in the control group. The carriers of C alleles presented with lower thickness of subcutaneous tissue and higher concentrations of HDL-C than the wild type. The incidence of MetS was 33% of the group of obese children. Analysis of the presence of MetS factors showed that there is more frequent MetS in the group with the wild homozygous genotype type.
Conclusion: Polymorphism 174G>C in the IL-6 gene does not seem to be associated with obesity and with the incidence of MetS in children.
Figures
References
-
- Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C. et al.Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006;17:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Barsh GS, Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S. Genetics of bodyweight regulation. Nature. 2000;404:644–651. - PubMed
-
- Popko K, Gorska E, Potapinska O. et al.Frequency of distribution of inflammatory cytokines IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α gene polymorphism in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;59(Suppl 6):607–614. - PubMed
-
- Chabowski A, Zmijewska M, Gorski J. et al.Effect of IL-6 deficiency on myocardial expression of fatty acid transporters and intracellular lipid deposits. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007;58(Suppl 5):73–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical