Anti-inflammatory effects of Myrtol standardized and other essential oils on alveolar macrophages from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 20156758
- PMCID: PMC3521325
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-14-s4-205
Anti-inflammatory effects of Myrtol standardized and other essential oils on alveolar macrophages from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Introduction: Myrtol standardized is established in the treatment of acute and chronic bronchitis and sinusitis. It increases mucociliar clearance and has muco-secretolytic effects. Additional anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties have been confirmed for Myrtol standardized, eucalyptus oil, and orange oil in several in vitro studies.
Objective: The aim of this study was to prove the ability of essential oils to reduce cytokines release and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production derived from ex vivo cultured alveolar macrophages.
Material and methods: Alveolar macrophages from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, n=26, GOLD III-IV) were pre-cultured with essential oils (10(3)-10(-8)%) for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 microg/ml). After 4 h and 20 h respectively a) cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) using 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein (DCF), and b) TNF-alpha, IL-8, and GM-CSF secretion were quantified.
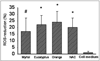
Results: In comparison with negative controls, pre-cultured Myrtol, eucalyptus oil and orange oil (10-4%) reduced in the LPS-activated alveolar macrophages ROS release significantly after 1+20 h as follows: Myrtol -17.7% (P=0.05), eucalyptus oil -21.8% (P<0.01) and orange oil -23.6% (P<0.01). Anti-oxidative efficacy was comparable to NAC (1 mmol/l). Essential oils also induced a TNF-alpha reduction: Myrtol (-37.3%, P<0.001), eucalyptus oil (-26.8%, P<0.01) and orange oil (-26.6%, P<0.01). TNF-a reduction at 1+4 h and 1+20 h did not vary (Myrtol: -31.9% and -37.3% respectively, P= 0.372) indicating that this effect occurs early and cannot be further stimulated. Myrtol reduced the release of GM-CSF by -35.7% and that of IL-8 only inconsiderably.
Conclusions: All essential oils tested have effective antioxidative properties in ex vivo cultured and LPS-stimulated alveolar macrophages. Additionally, Myrtol inhibited TNF-a and GM-CSF release best indicating additional potent anti-inflammatory activity.
Figures
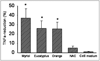

References
-
- Rabe KF, Hurd SS, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Buist SA, Calverley PMA, Fukuchi Y, Jenkins C, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Weel van C, Zielinski J. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. GOLD Executive Summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:532–55. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200703-456SO. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO report of an expert committee: Definition and diagnosis of pulmonary disease with special reference to chronic bronchitis and emphysema. WHO Techn Rep Ser. 1961;213:14–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
