Dynamic regulation of a metabolic multi-enzyme complex by protein kinase CK2
- PMID: 20157113
- PMCID: PMC2856985
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101139
Dynamic regulation of a metabolic multi-enzyme complex by protein kinase CK2
Abstract
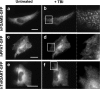
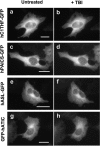
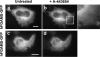
The reversible association and dissociation of a metabolic multi-enzyme complex participating in de novo purine biosynthesis, the purinosome, was demonstrated in live cells to respond to the levels of purine nucleotides in the culture media. We also took advantage of in vitro proteomic scale studies of cellular substrates of human protein kinases (e.g. casein kinase II (CK2) and Akt), that implicated several de novo purine biosynthetic enzymes as kinase substrates. Here, we successfully identified that purinosome formation in vivo was significantly promoted in HeLa cells by the addition of small-molecule CK2-specific inhibitors (i.e. 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzimidazole, 2-dimethylamino-4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzimidazole, tetrabromocinammic acid, 4,4',5,5',6,6'-hexahydroxydiphenic acid 2,2',6,6'-dilactone (ellagic acid) as well as by silencing the endogenous human CK2alpha catalytic subunit with small interfering RNA. However, 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole, another CK2-specific inhibitor, triggered the dissociation of purinosome clusters in HeLa cells. Although the mechanism by which 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole affects purinosome clustering is not clear, we were capable of chemically reversing purinosome formation in cells by the sequential addition of two CK2 inhibitors. Collectively, we provide compelling cellular evidence that CK2-mediated pathways reversibly regulate purinosome assembly, and thus the purinosome may be one of the ultimate targets of kinase inhibitors.
Figures


References
-
- Rowe P. B., McCairns E., Madsen G., Sauer D., Elliott H. (1978) J. Biol. Chem. 253, 7711–7721 - PubMed
-
- Smith G. K., Mueller W. T., Wasserman G. F., Taylor W. D., Benkovic S. J. (1980) Biochemistry 19, 4313–4321 - PubMed
-
- Srere P. A. (1987) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56, 89–124 - PubMed
-
- An S., Kumar R., Sheets E. D., Benkovic S. J. (2008) Science 320, 103–106 - PubMed
-
- Meggio F., Pinna L. A. (2003) FASEB J. 17, 349–368 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

