Progressive age-related impairment of the late long-term potentiation in Alzheimer's disease presenilin-1 mutant knock-in mice
- PMID: 20157256
- PMCID: PMC2891870
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1302
Progressive age-related impairment of the late long-term potentiation in Alzheimer's disease presenilin-1 mutant knock-in mice
Abstract
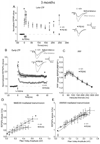
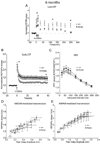
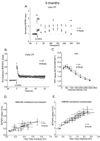
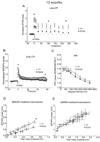
Presenilin 1 (PS1) mutations are responsible for many early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD) cases. While increasing evidence points to impaired synaptic plasticity as an early event in AD, PS1 mutant mice exhibit a paradoxical increase in hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP). Among PS1 mouse models, PS1 M146V mutant knock-in mice (PS1KI) are particularly interesting in that they exhibit memory impairment in spatial tasks. Here we investigated the effects of aging on two forms of LTP in PS1KI mice, the widely-studied early phase of LTP (E-LTP) and a particular form of LTP called late-LTP (L-LTP) which requires transcription and protein synthesis. L-LTP is thought to be critical for long-term memory. We found a lower L-LTP maintenance phase in PS1KI mice compared to wild type littermates at 3 months of age. As the mice age, they exhibit impairment of both the induction and maintenance phases of LTP. When E-LTP and NMDA receptor-mediated transmission were analyzed, PS1KI mice displayed an increase at 3 months compared to wild type littermates; this difference did not persist at older ages and finally decreased at 12 months. These results reveal an L-LTP decrease in PS1 mutant mice at an early stage, which occurs coincidently with a paradoxical enhancement of E-LTP. The observation of a decrease in both forms of LTP during aging supports the view that PS1KI mice are a valuable model for the study of age-dependent synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline in AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-dependent impairment of spine morphology and synaptic plasticity in hippocampal CA1 neurons of a presenilin 1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2009 Aug 12;29(32):10144-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1856-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19675248 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin-1 mutation impairs cholinergic modulation of synaptic plasticity and suppresses NMDA currents in hippocampus slices.Neurobiol Aging. 2009 Jul;30(7):1061-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.10.009. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Neurobiol Aging. 2009. PMID: 18068871 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signaling, excitability, and synaptic plasticity defects in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(2):561-80. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142427. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25589721 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin transgenic mice as models of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Mar;214(2-3):127-43. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0227-3. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 19921519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-related progressive synaptic dysfunction: the critical role of presenilin 1.Rev Neurosci. 2010;21(4):239-50. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2010.21.4.239. Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21086758 Review.
Cited by
-
Disturbed calcium signaling in spinocerebellar ataxias and Alzheimer's disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Apr;40:127-33. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25846864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMDA Neurotransmission Dysfunction in Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2012 Sep;10(3):272-85. doi: 10.2174/157015912803217288. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23450042 Free PMC article.
-
Store-Operated Calcium Channel Complex in Postsynaptic Spines: A New Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.J Neurosci. 2016 Nov 23;36(47):11837-11850. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1188-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27881772 Free PMC article.
-
Extract of Fructus Cannabis Ameliorates Learning and Memory Impairment Induced by D-Galactose in an Aging Rats Model.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:4757520. doi: 10.1155/2017/4757520. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29234402 Free PMC article.
-
IL-37 expression reduces acute and chronic neuroinflammation and rescues cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.Elife. 2022 Aug 30;11:e75889. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75889. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36040311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chapman PF, White GL, Jones MW, Cooper-Blacketer D, Marshall VJ, Irizarry M, Younkin L, Good MA, Bliss TV, Hyman BT, Younkin SG, Hsiao KK. Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Walsh DM, Klyubin I, Fadeeva JV, Cullen WK, Anwyl R, Wolfe MS, Rowan MJ, Selkoe DJ. Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid beta protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature. 2002;416:535–539. - PubMed
-
- Parent A, Linden DJ, Sisodia SS, Borchelt DR. Synaptic transmission and hippocampal long-term potentiation in transgenic mice expressing FAD-linked presenilin 1. Neurobiol Dis. 1999;6:56–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

